Food & Body


news
More Links Between Gut Health & Autism as 'Probiotic' Transplant Trials Show Some Success
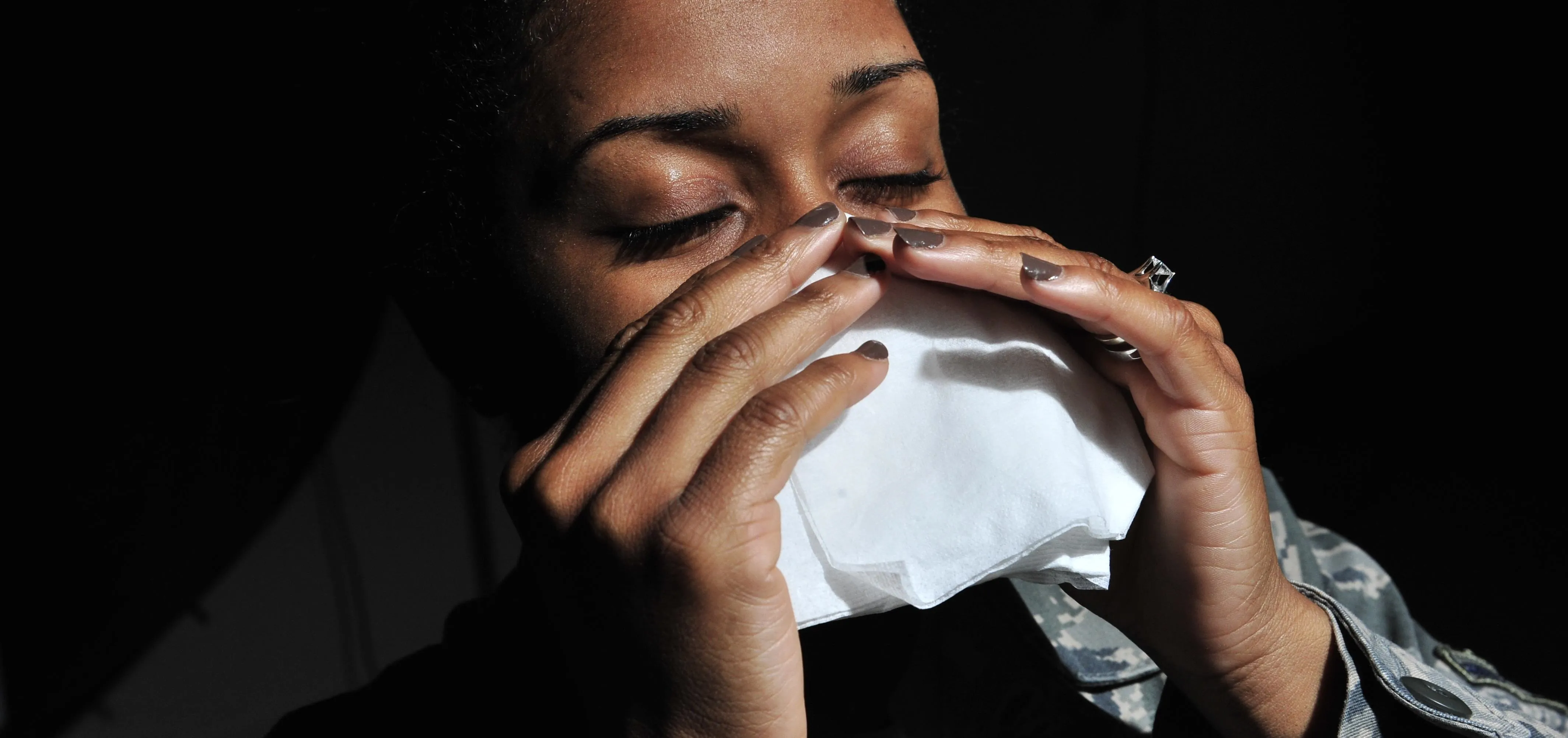


how to
Clear Your Stuffy Sinuses in Seconds Using Nothing but Pressure
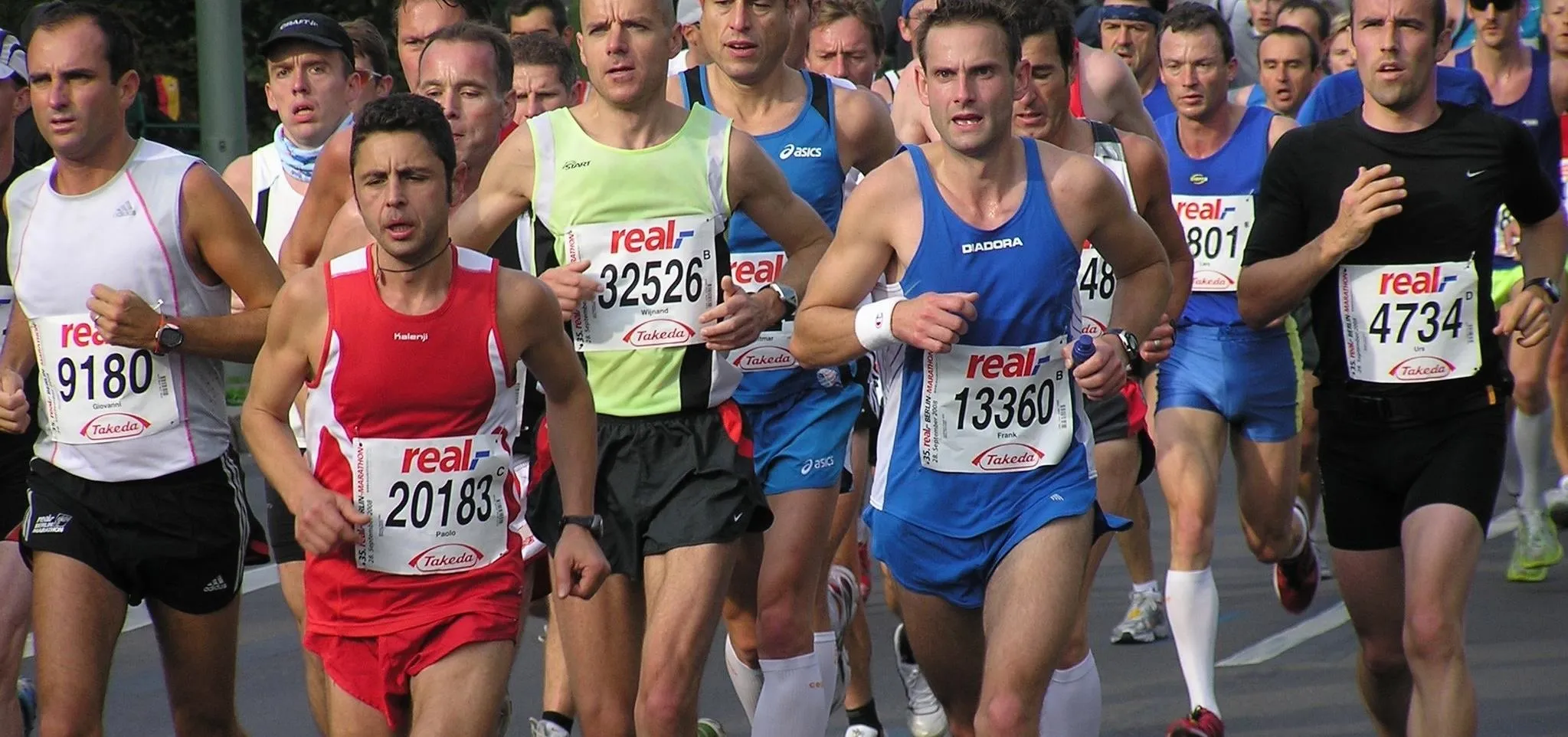


news
Survival of the Fittest: Athletes' Gut Microbes Are Tailored to Help Them Compete





























Featured On WonderHowTo:
Productivity & Shortcuts










Featured On WonderHowTo:
Music & Audio










Featured On WonderHowTo:
Augmented Reality










Featured On WonderHowTo:
Gaming