Animals


News: Tardigrades Are the Earth's Toughest & Almost-Immortal Animals
Tardigrades are some of the toughest but least well-known creatures on our planet. These tiny animals, also called moss piglets or water bears, are definitely of this earth, but some can boast that they've also traveled to space.
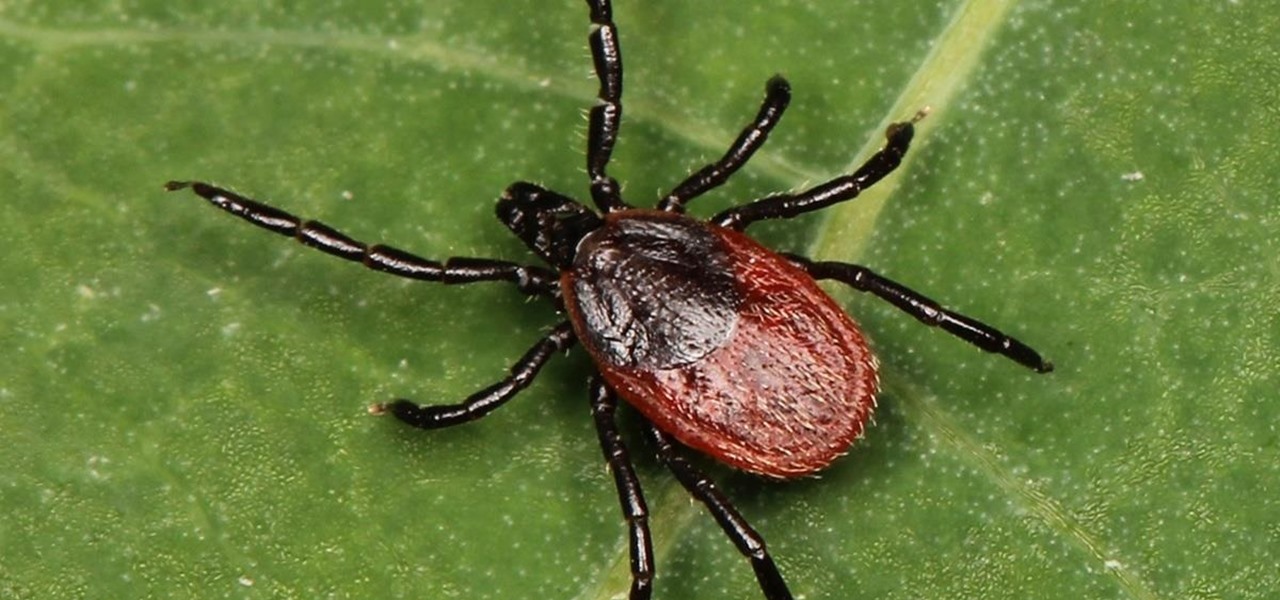

News You Can Use: Map Shows Where Dogs & Humans Are at High Risk of Lyme Disease This Summer
Lyme is a growing threat as we move into warmer weather in the US. Researchers have said this year could be one of the worst for this tick-borne disease, as a skyrocketing mouse population and warmer temperatures increase the risk.

News: Deadly Lungworm Parasite Spread by Rats & Snails Is More Prevalent Than We Thought
Deadly rat lungworm parasites have found their way into Florida. The parasitic worm relies on snails and rats to complete its life cycle, but don't let this nematode's name fool you. This worm can cause meningitis and death in humans who inadvertently consume snails, frogs, or crustaceans harboring the infective parasite.

News: Another Good Reason to Keep Your Cat Indoors — Tick Bites Can Kill
Like humans, cats can suffer infections caused by ticks, and too often, the disease is fatal. Learn about tickborne diseases that affect cats and what you can do to protect Fluffy from an untimely demise.

News: Arizona Woman Dies After Catching Tularemia from Her Dog
On June 11, 2016, an Arizona woman died from what appeared to be several infections, including pneumonia. She likely caught at least one of these from her dog.
News: Bed Bugs Are Becoming Resistant to All of Our Insecticides—This Fungus Might Help
If you have encountered bed bugs lately, you are not alone. While the pesticides used to fight these pests are losing effectiveness, a fungus shows promise in knocking the bugs out of beds everywhere.

News: Dogs Could Be Spreading Antibiotic-Resistant Infections to Their Owners
Our canine best friends could spread our bacterial worst nightmare, according to a recent study. The problem with drug-resistant bacteria is well known. Overused, poorly used, and naturally adaptive bacteria clearly have us outnumbered. As science drives hard to find alternative drugs, therapies, and options to treat increasingly resistant infections, humans are treading water, hoping our drugs of last resort work until we figure out better strategies.
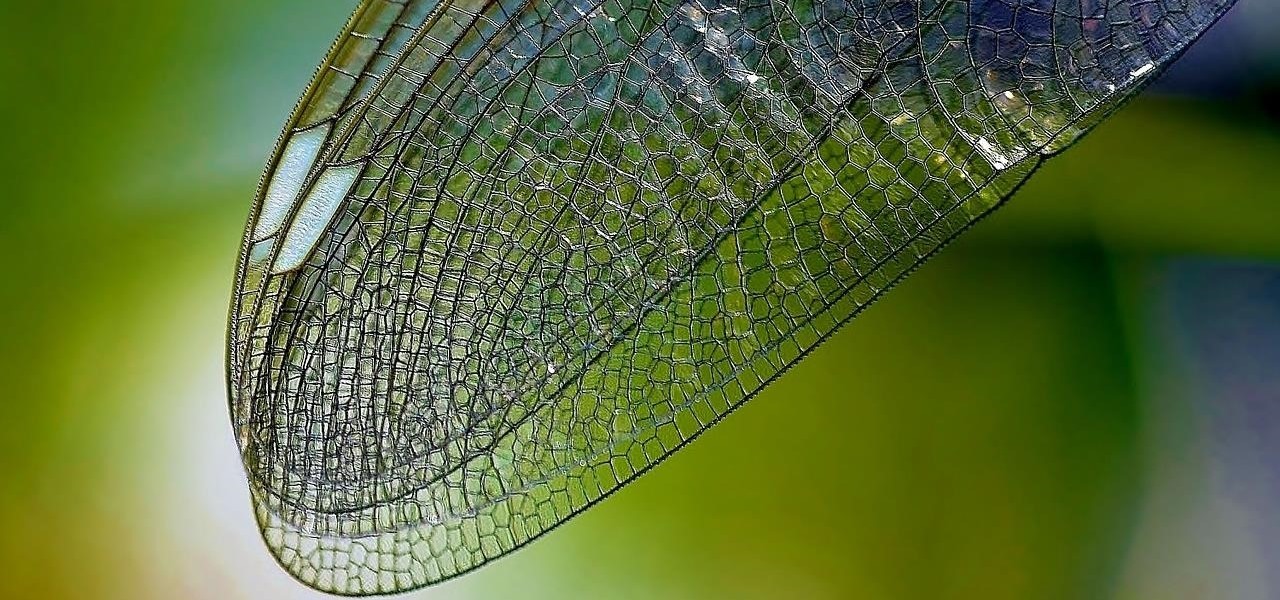

News: Scientists Are Using the Special Physics of Dragonfly Wings to Create Surfaces That Shred Bacteria on Contact
As drug-resistant bacteria become more commonplace, researchers are looking for new antibacterial strategies to disrupt disease-causing microbes. Some scientists are working to create new drugs, while others are trying out drug combinations. Another group, however, are ditching pharmaceuticals altogether and experimenting with non-drug alternatives.

News: How Livestock Farts Lead to a Warmer Climate
When it comes to global warming, most of us think of carbon dioxide emissions. While carbon dioxide is the most important greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide emissions have stayed constant for the last three years. On the other hand, methane, the second most important gas, has been steadily rising since 2007.

News: Bubonic Plague Is on the Rise in the US, but We Finally Know How to Treat It
Yes, bubonic plague—the Black Death that killed millions in the Middle Ages— is still out there. It even infects and kills people in the United States. Without treatment, half the people infected die, but the Food and Drug Administration approved ciprofloxacin in 2015 to treat plague, and it has just successfully been used to stop the infection in five people.

News: Flesh-Eating Bacteria from Cat Scratch Leads to Death for Man in Thailand
Phuket, the island in Thailand typically associated with paradise and most recently, illegally-run hotels, now has a different problem—a stray cat with the claws of death.

News: Mass Die-Off of Thousands of Ducks in Idaho Caused by Avian Cholera
Over 6,500 waterfowl—mostly ducks—have died in Canyon County, Idaho, stricken by avian cholera. The outbreak started in February, and before it's over, it may not only be Idaho's largest outbreak, but one of the largest in the country.
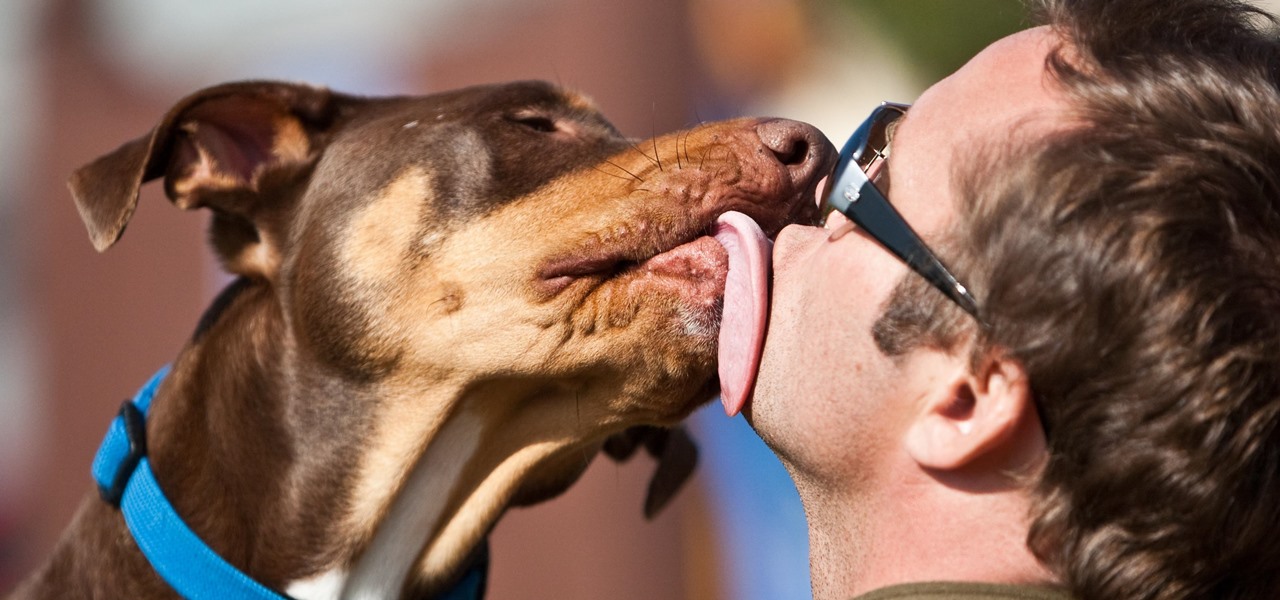

News: We Know You Want To, but You Really Shouldn't Be Kissing Your Pet on the Mouth
If you live with pets, you know where their tongue has been, yet you let them kiss and lick you all they want without even thinking twice about it. I've heard people say that a dog's mouth is very clean, and that their saliva, delivered by licking, can help heal wounds, but is that really true?
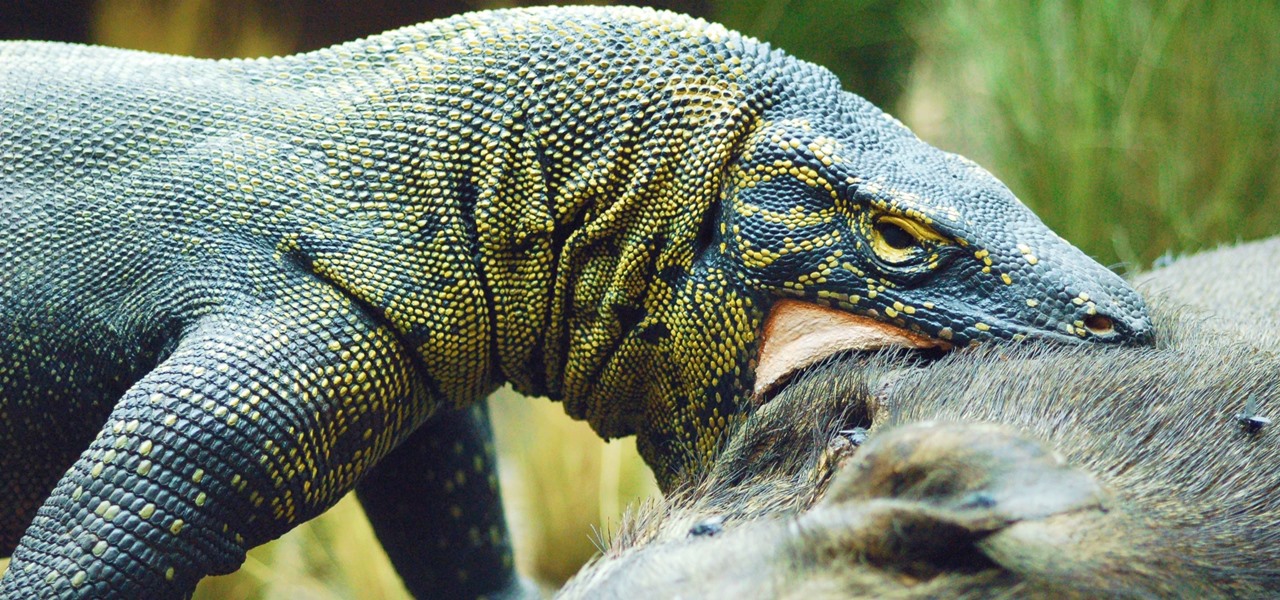

News: The Magic of Komodo Dragon Blood: The Stuff Legends — & Antibiotics — Are Made Of
Despite legends to the contrary, it appears that the saliva of a Komodo dragon is not teeming with pathogenic bacteria that kills their prey. Its reputation to survive while colonized with lots of horrible disease-causing bacteria, true or untrue, has made it the subject of research in pursuit of natural antimicrobial agents and led scientists to some remarkable findings.

News: How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs Using Less Pesticide
Bed bugs are parasites not yet known to spread disease — but they cause plenty of irritation. As scientists and landlords search for new ways to deal with the pests, a new study examines how we can deter bed bugs without so many chemicals.
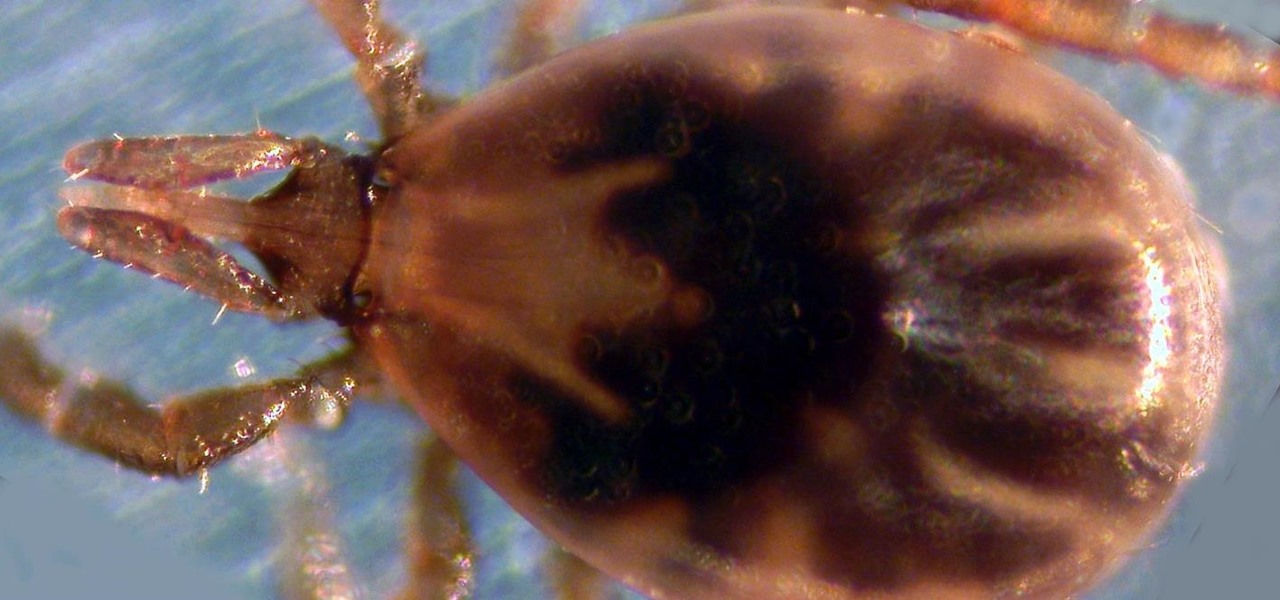

News: Visiting a National Park in the East? Watch for Lyme-Spreading Ticks
Transmitted by ticks, Lyme disease is a serious infection that is probably headed your way. A recent study confirms the pathogen that causes Lyme disease is now established in nine national parks in the East, including Acadia and Shenandoah National Parks.

News: Bed Bugs Are in a Lot of Hotel Rooms — Here's How to Spot Them
Bed bugs are brown and creepy. Could you spot one in your hotel room? A new study reveals most people are freaked out by bed bugs, but only about 35% could identify one.

News: Potentially Serious Flea-Spread Disease Expanding Its Territory in Texas
A sometimes serious disease spread by fleas is making inroads in Texas, quietly doubling case numbers since 2008, and beginning to encroach on larger metropolitan areas.

News: Research Published in mBio Shows How Gut Bacteria Can Help Chubby Dogs Live a Better—& Longer—Life
As fun as it is to see Fido's face light up when you feed him table scraps, American dogs are getting fat. The good news is that research is homing in on nutritional strategies to boost canine capabilities to maintain a healthy weight.

News: New Map Shows Where Zika Mosquitoes Live in the US
As summer heats up, new maps from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) gives us our best guess at where Zika-carrying mosquitoes could be hanging out this year in the US.