Innovation


news
In the Ultimate Irony, Zika Virus May Cure Brain Cancer


news
Scientists Turn Bacteria into Mini Cyborg Solar Panels


news
Monthly Injection Has Potential to Replace Daily Handfuls of HIV Drugs





























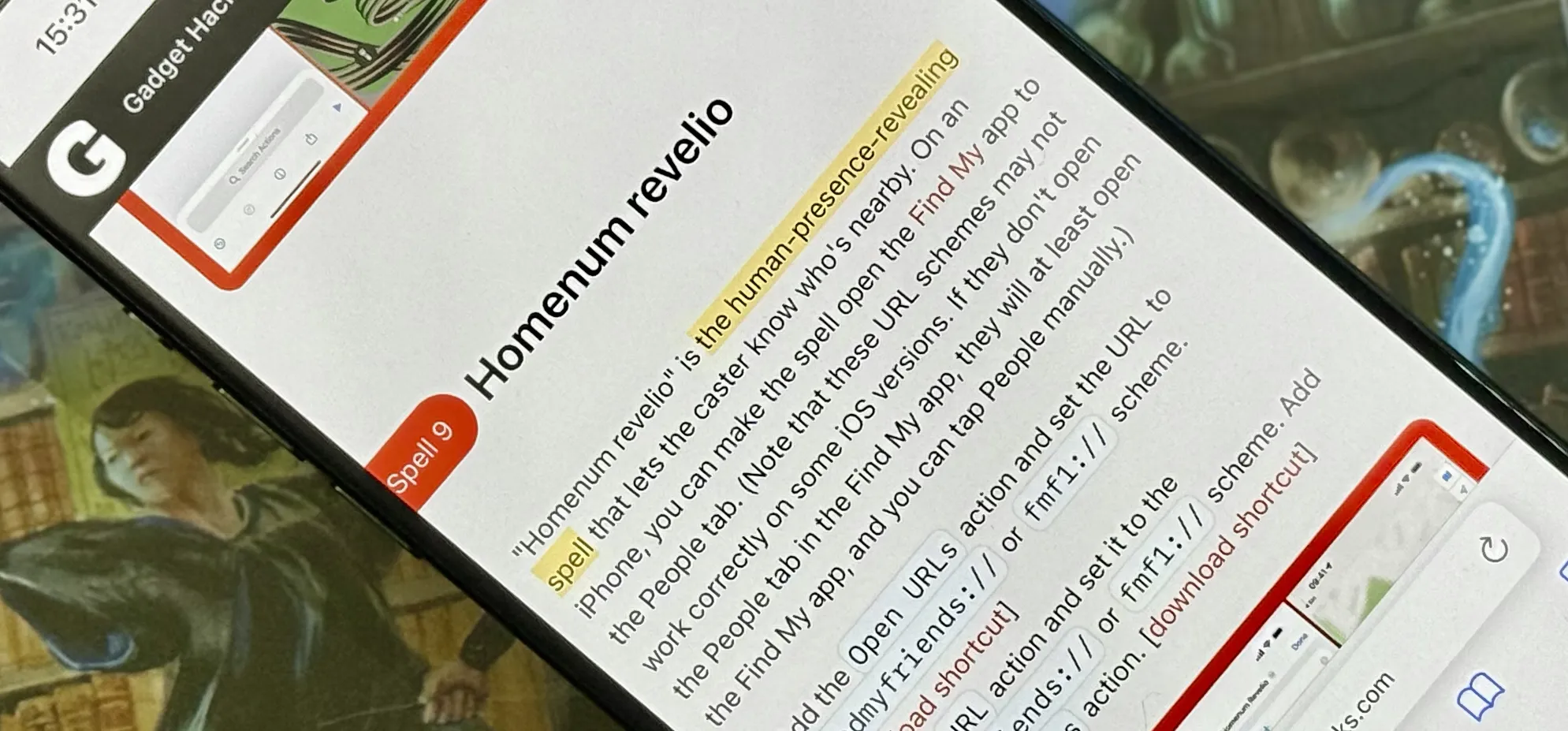
Featured On WonderHowTo:
Productivity & Shortcuts










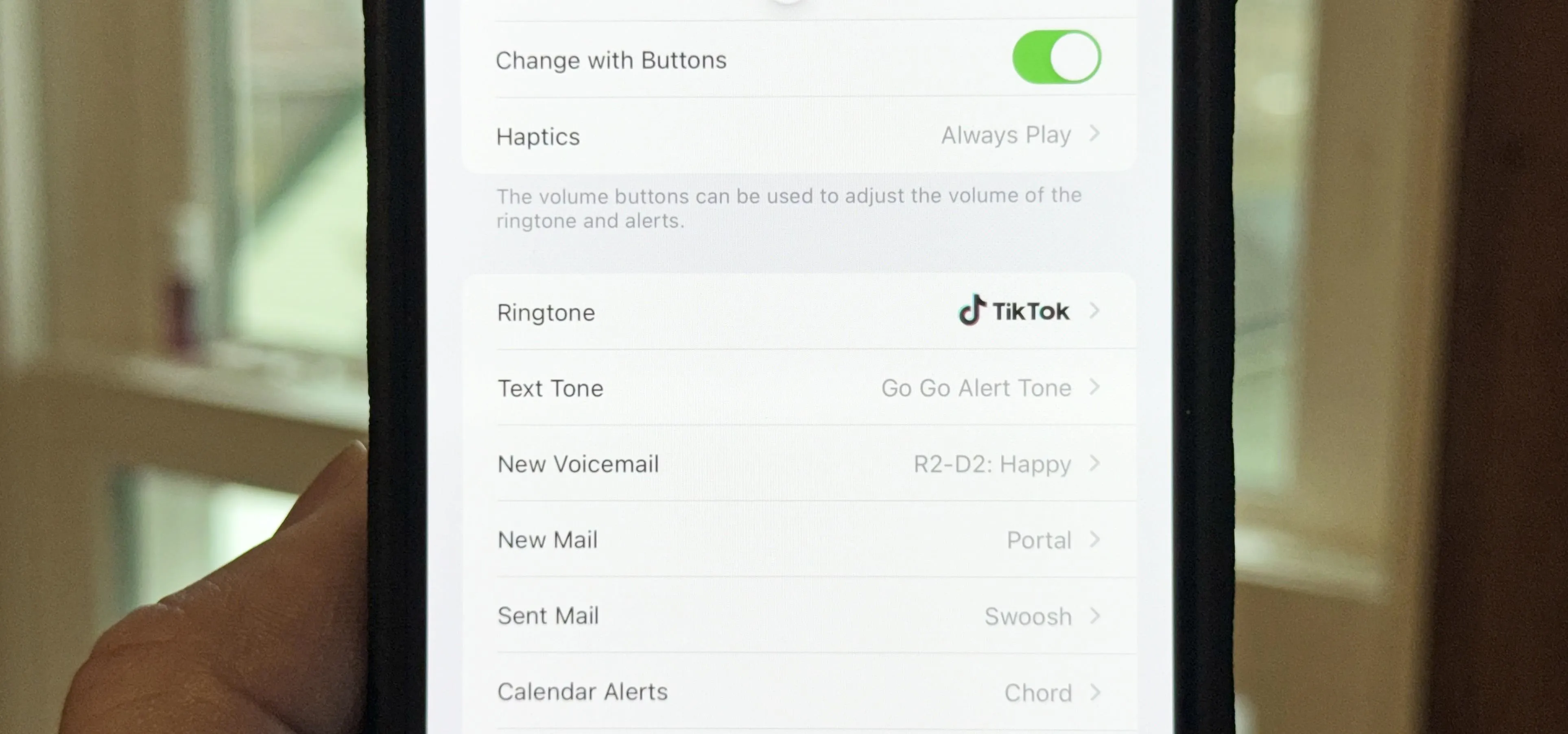
Featured On WonderHowTo:
Music & Audio










Featured On WonderHowTo:
Augmented Reality










Featured On WonderHowTo:
Gaming