Superbugs





























Featured On WonderHowTo:
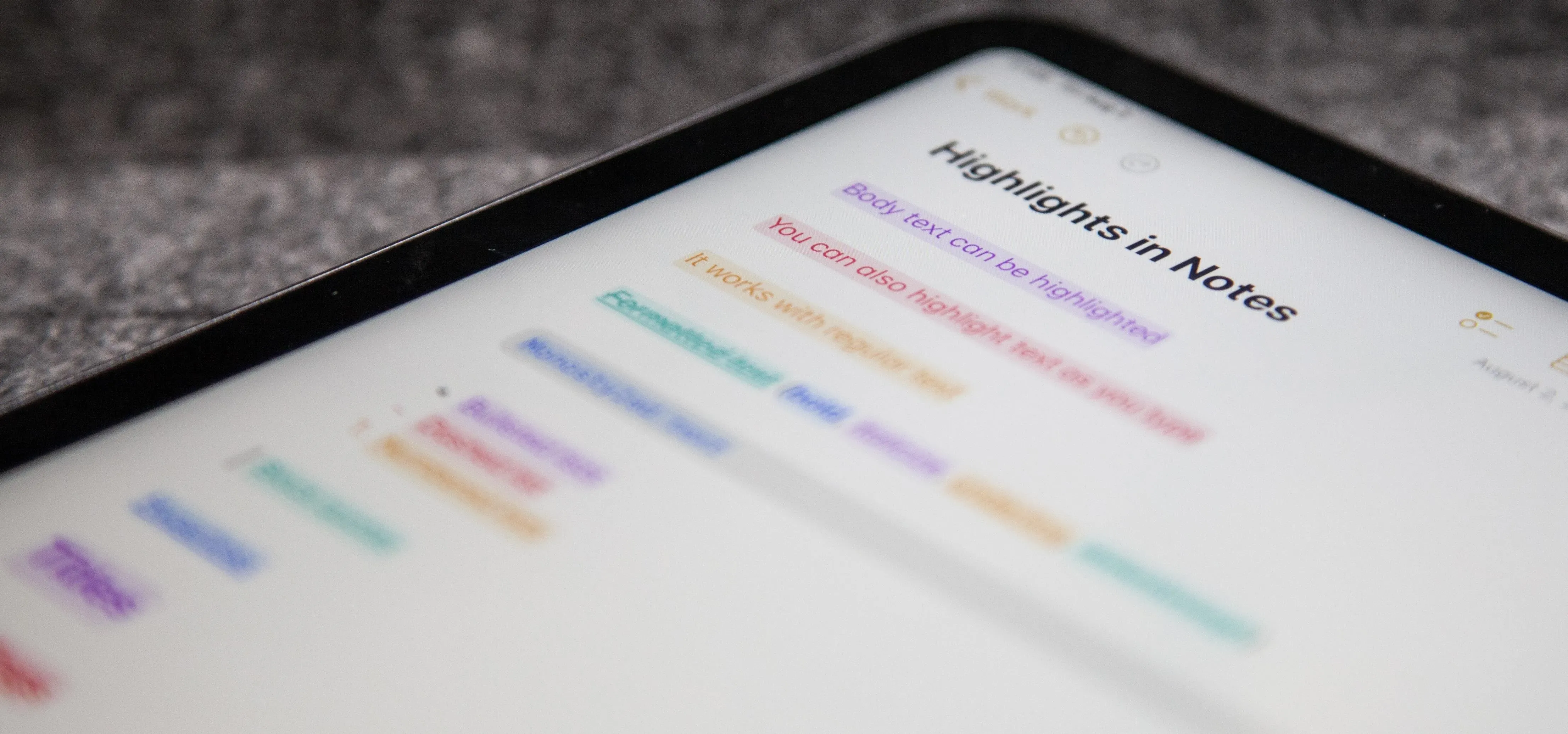
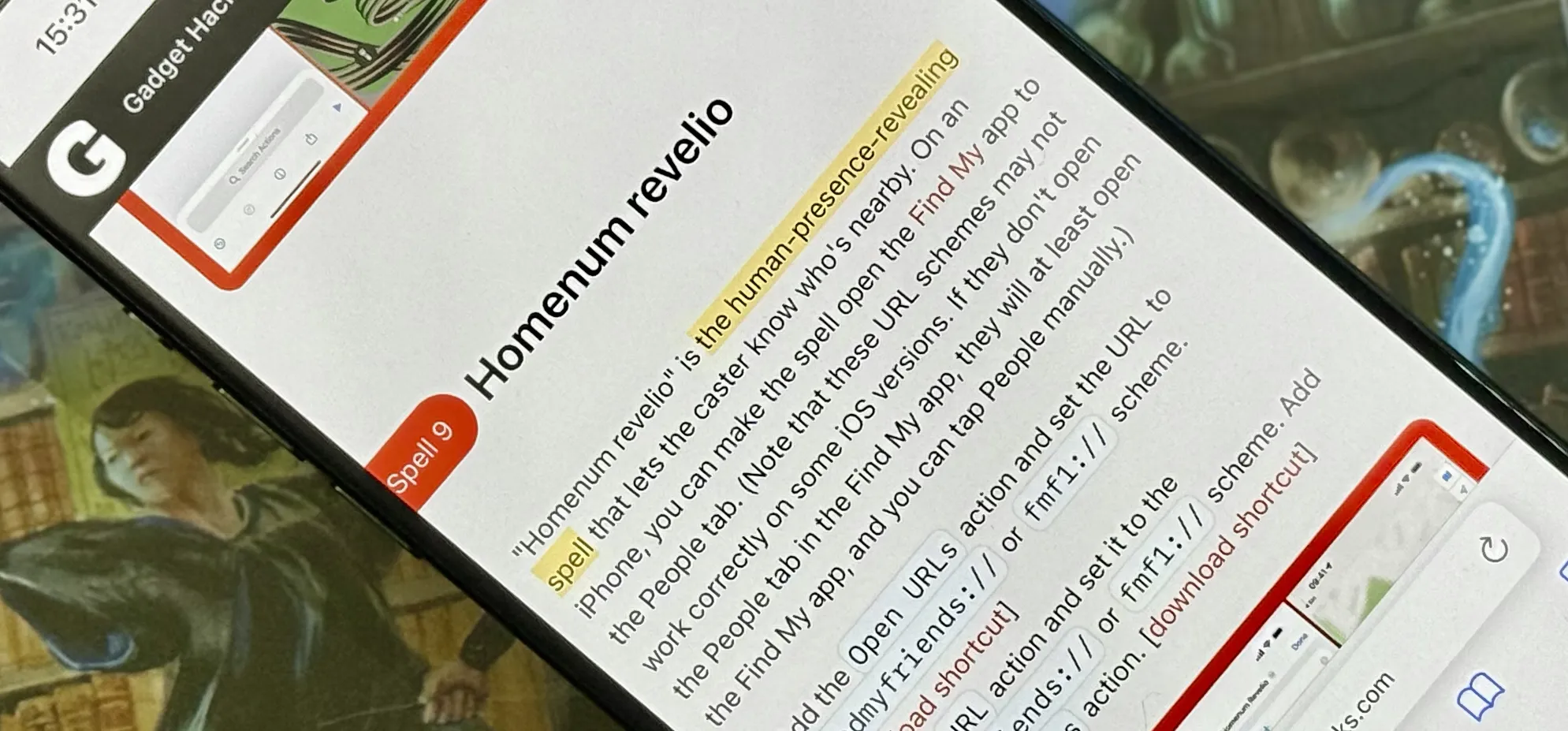
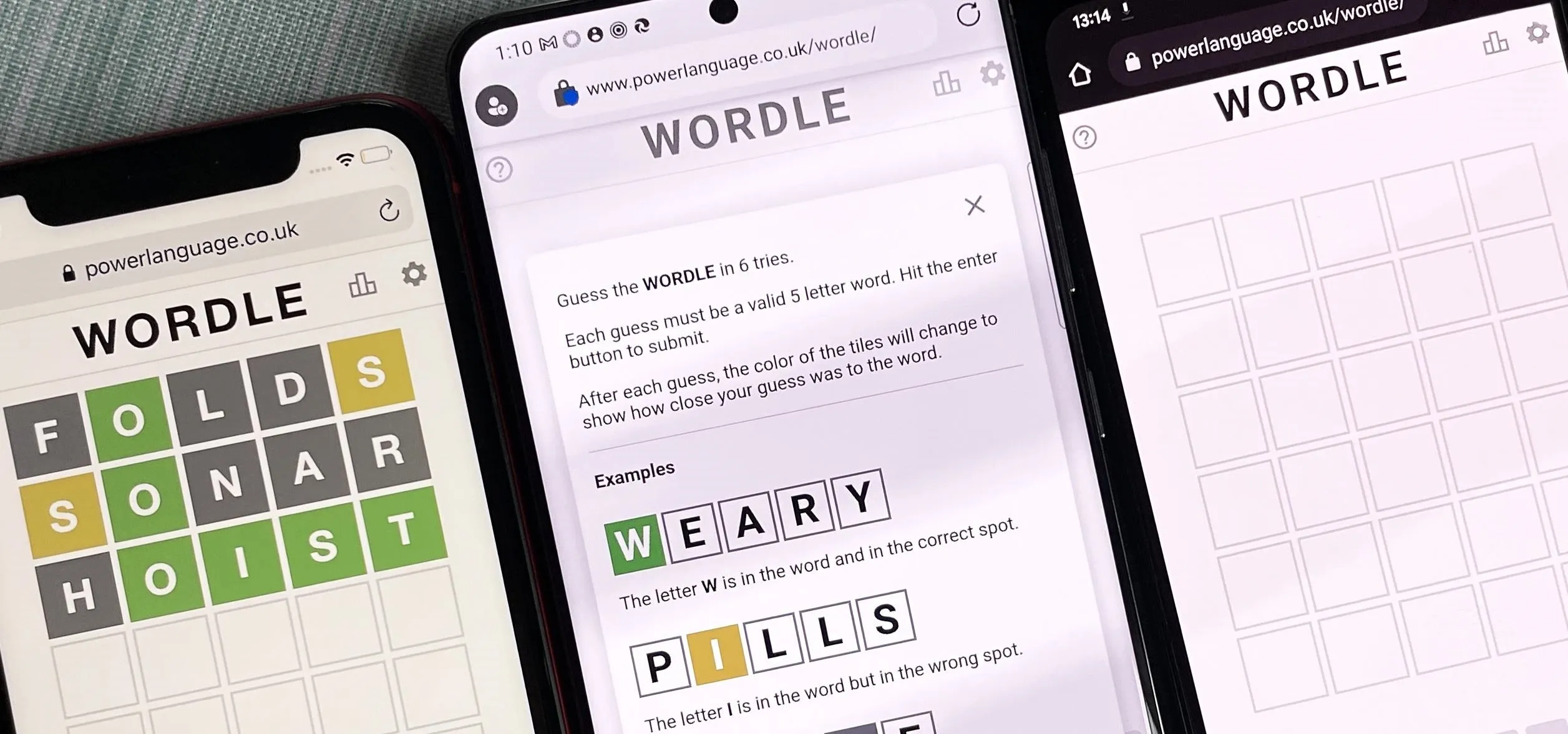
Productivity & Shortcuts










Featured On WonderHowTo:
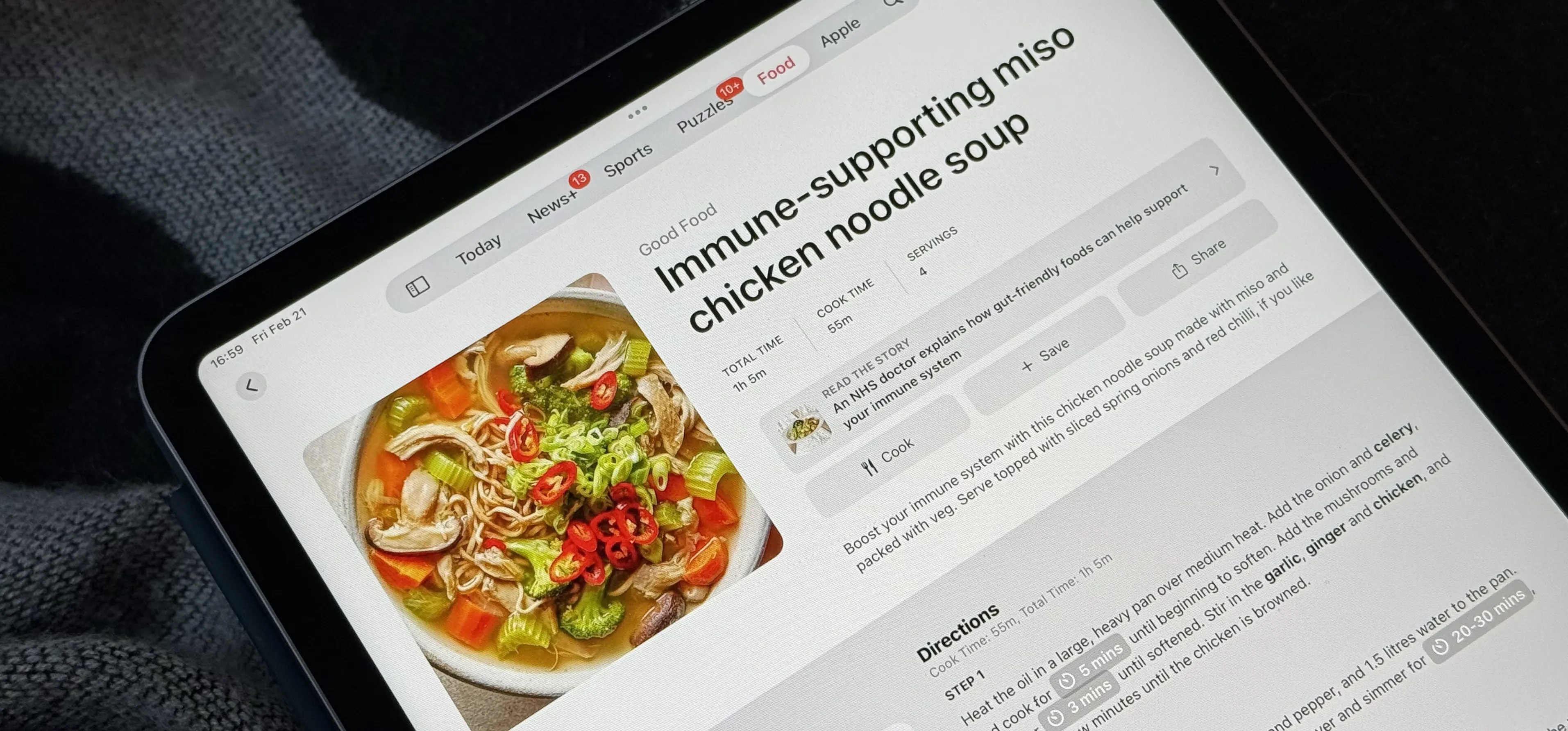
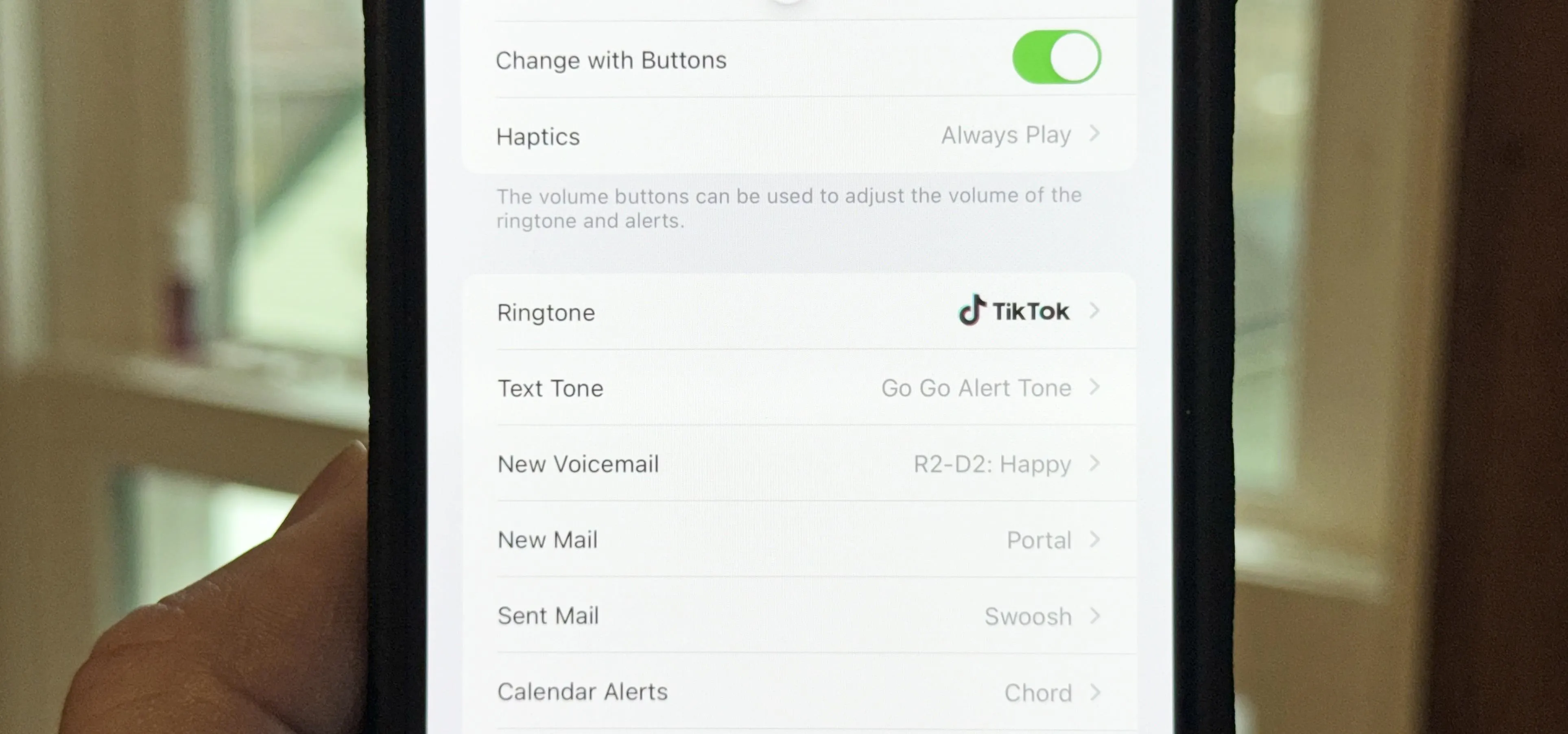
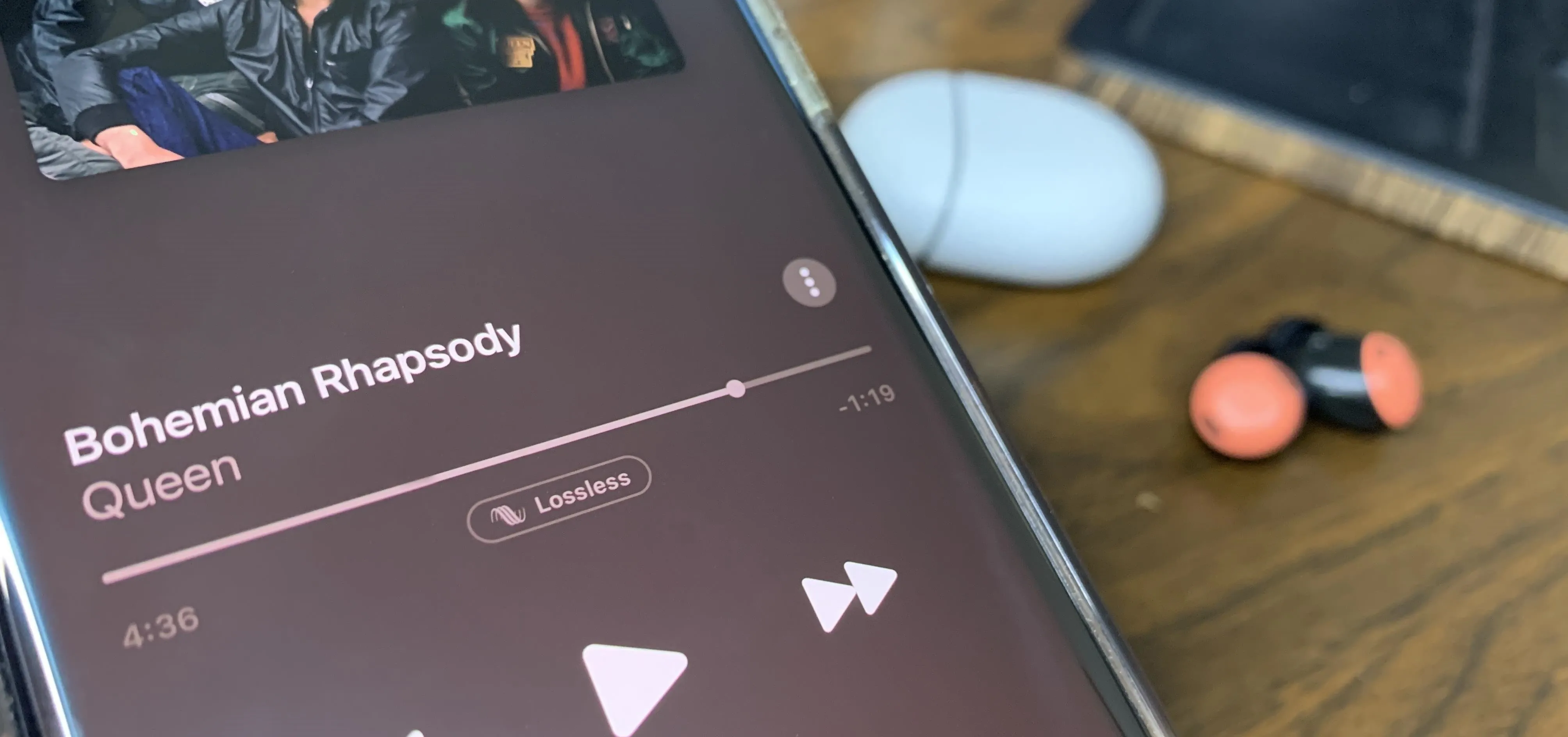
Music & Audio










Featured On WonderHowTo:
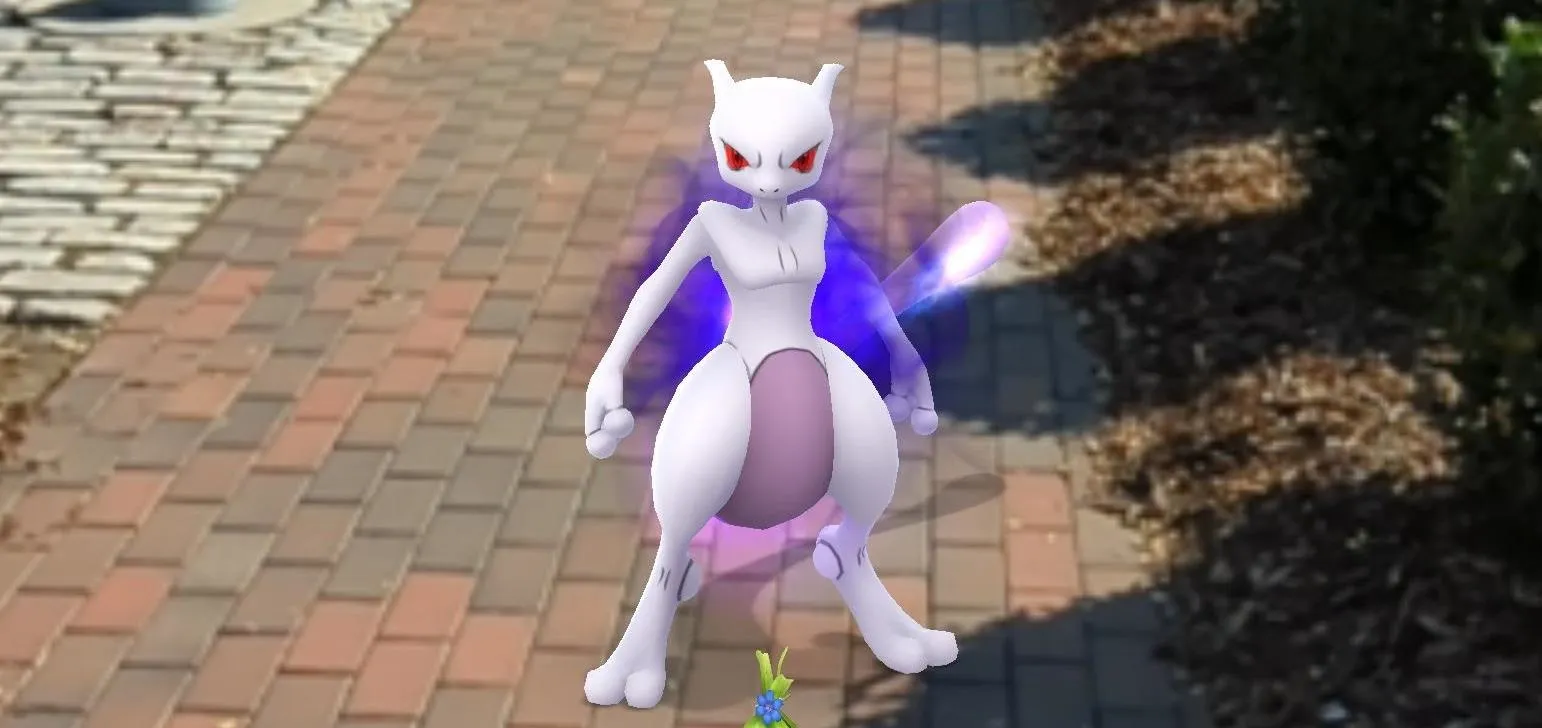
Augmented Reality










Featured On WonderHowTo:
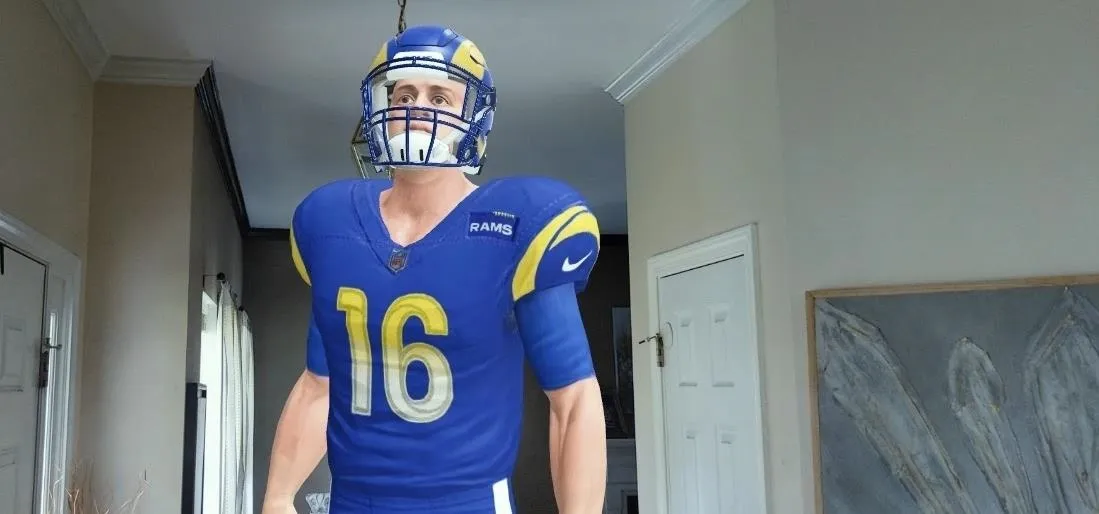
Gaming