Hot Invisiverse Posts


News: Latest Research Cements Link Between Climate Change & West Nile Outbreaks
A recent study underscores a connection between climate change and infectious disease, raising concerns about our quickly warming planet.
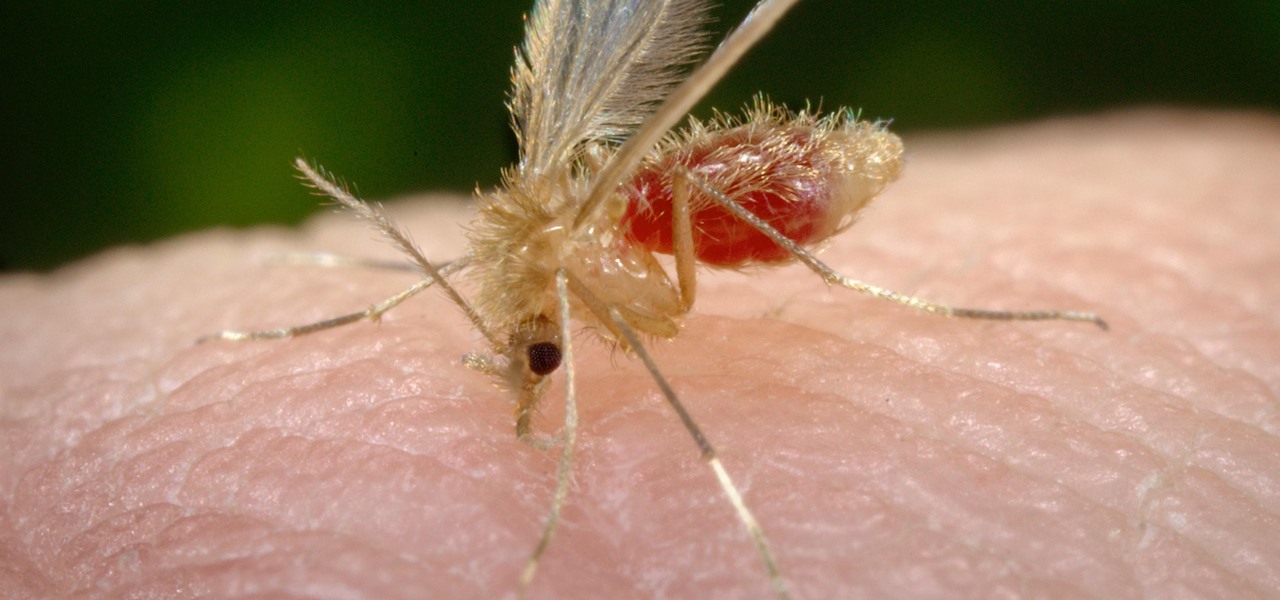

News: New Research Shows How Flesh-Eating Leishmania Parasites Hide in Our Bodies to Fight Future Infections
Transmitted by a sandfly one-third the size of a mosquito, parasitic Leishmania protozoa are responsible for a flesh-destroying disease that kills an estimated 20,000 people per year. Two new studies offer understanding of how the parasite provides immunity through persistence and why some people suffer more virulent forms of the disease.

Tips for Cold Season: How to Spread Fewer Germs When Sneezing
What's in a sneeze? Quite a lot—dirt, mucus, and infectious germs—it seems. And sneezing the right way can reduce the germs you share with neighbors.

News: Researchers Have Just Discovered How a Hospital Fungus Forms Slime, Becomes Drug Resistant & Kills Patients
It hasn't even been eight years since Candida auris was discovered—cultured and identified from the ear canal of a patient in Japan—and now it's drug-resistant, setting up residence in hospitals, killing patients, and wreaking havoc across the globe.

News: Research Published in mBio Shows How Gut Bacteria Can Help Chubby Dogs Live a Better—& Longer—Life
As fun as it is to see Fido's face light up when you feed him table scraps, American dogs are getting fat. The good news is that research is homing in on nutritional strategies to boost canine capabilities to maintain a healthy weight.
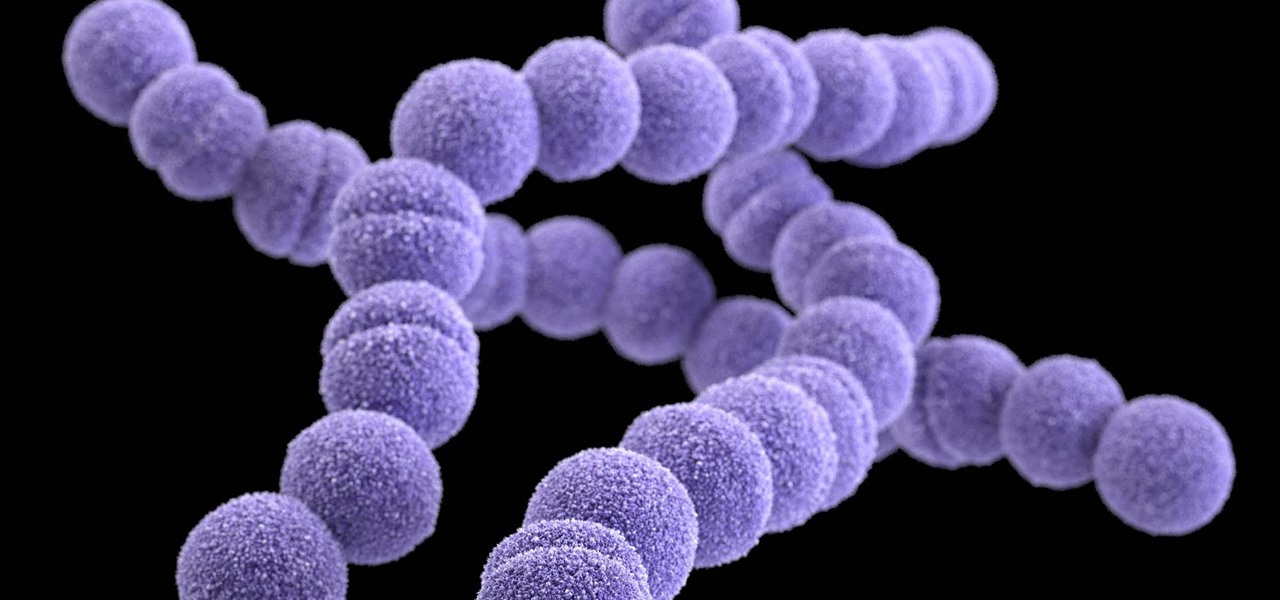
News: New Finding Shows How Deadly, Flesh-Eating Strep Toxins Help the Bacteria Burrow Deeper into Tissues
Where in the world did it come from? All of a sudden, one day, someone had an infection with flesh-eating bacteria. It captured headlines and worldwide attention because it was such a severe, strange, uncontrollable, and really disgusting condition.

News: Chronically Missing Just 1 Hour of Sleep a Night Makes Your Body Ripe for Sickness, New Study Says
Sleep lets our body processes rest and restores us for the next day, so a bad night's sleep can ruin the following twenty-four hours and even make us feel sick. Now, new research published in the journal Sleep cements the idea that loss of sleep actually leaves us vulnerable to sickness.

News: Wine Research Study Reveals How to Make Better Booze by Dosing Yeast with Nitrogen
Ah, wine. The bouquet fills your nose. The rich finish fills your mouth with soft flavors of oak and raspberries. The wine warms your belly and soothes your mind. Yeast and their biochemical factory help create this feast for your senses. Thanks to a research group from France, we now have a little more information on how that process works and a little more appreciation for yeast's contribution.

News: New Study Says Stopping Slimy Biofilms Could Save Thousands a Year from Legionnaires' Disease
In the summer of 1976, 4,000 American Legionnaires descended upon the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for a four-day convention. Several days later, many of the attendees experienced symptoms of severe pneumonia. By the beginning of August, 22 people had died. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that about 180 people were sickened and 29 people died before this mysterious outbreak burnt out.

News: New JAMA Study Shows That Testing Gut Bacteria Can Predict Risk of Heart Attack
It feels like someone reached into your chest and squeezed. Your head throbs in unison with your heartbeat. Clammy dread coats your body in sweat. Whether you call 911 or someone does it for you, the ER is your next stop.
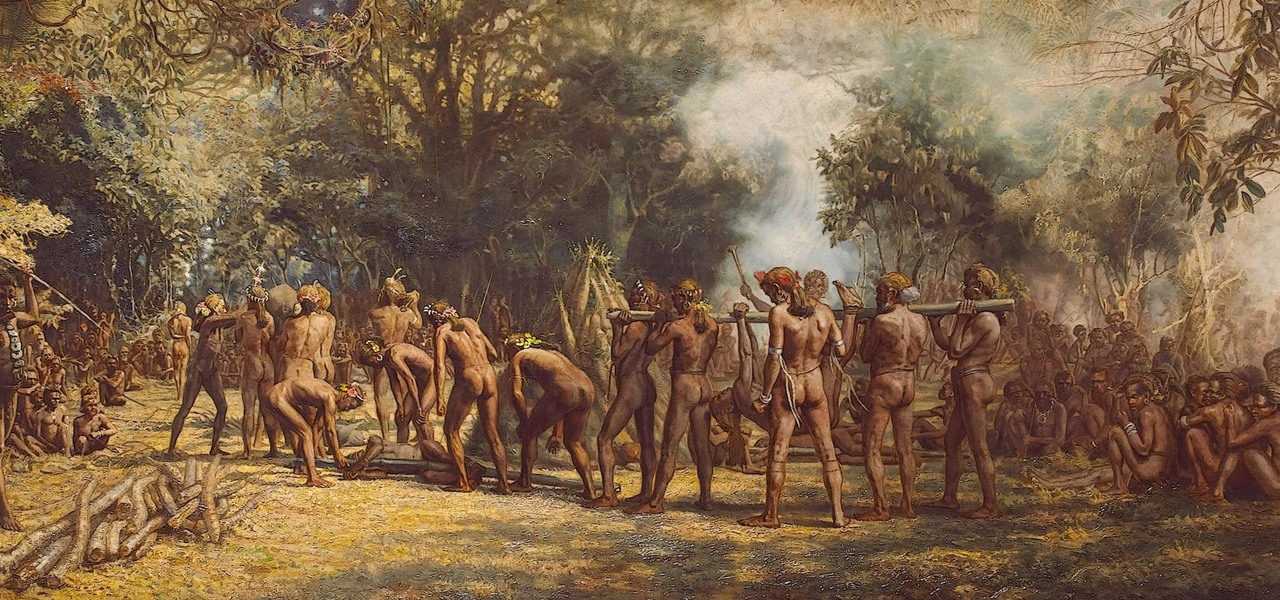

News: New Study Unveils the True Story of Kuru, a Fatal Brain Disease Spread by the Cultural Practice of Eating the Dead
Kuru is called the shaking disease, its name derived from the Fore word for "to shake." Caused by an organism that infects the part of the brain that controls coordination, people afflicted with kuru shake uncontrollably.
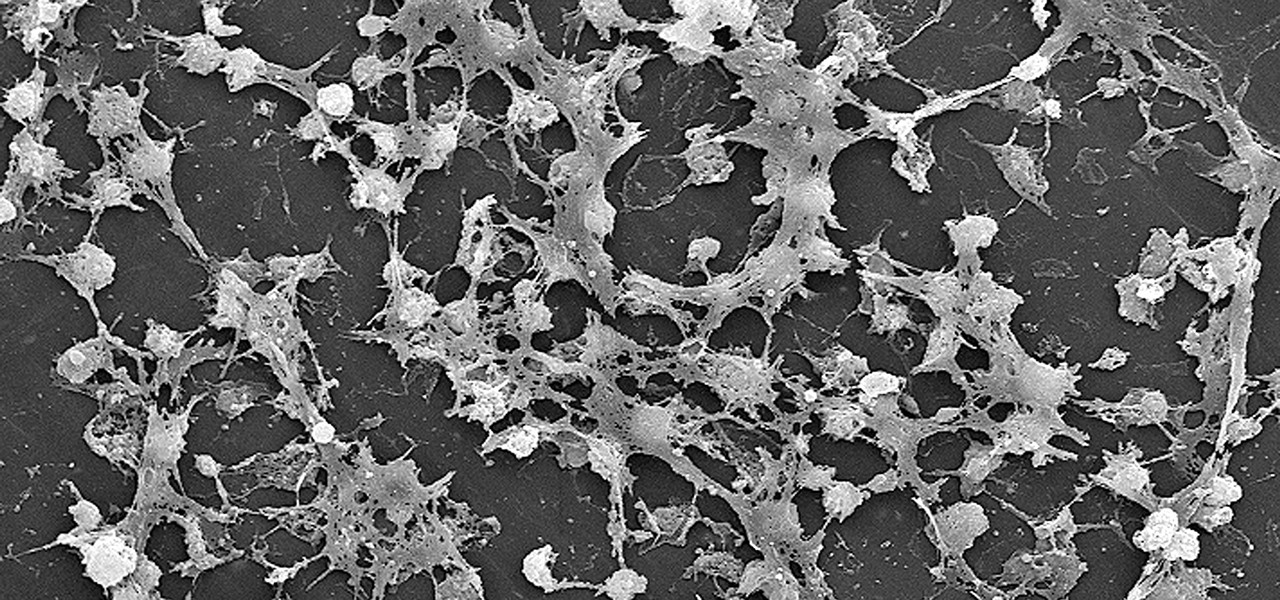
News: Dangerous Bacterial Films Communicate with Electric Pulses, Which Means We Could Zap Them to Interfere
Lighthouses and signal fires may have been the first social media. Without the ability to share language, a distant light meant "humans here." A new study from the University of California, San Diego, finds that bacteria can also send out a universal sign to attract the attention of their own, and other bacterial species.
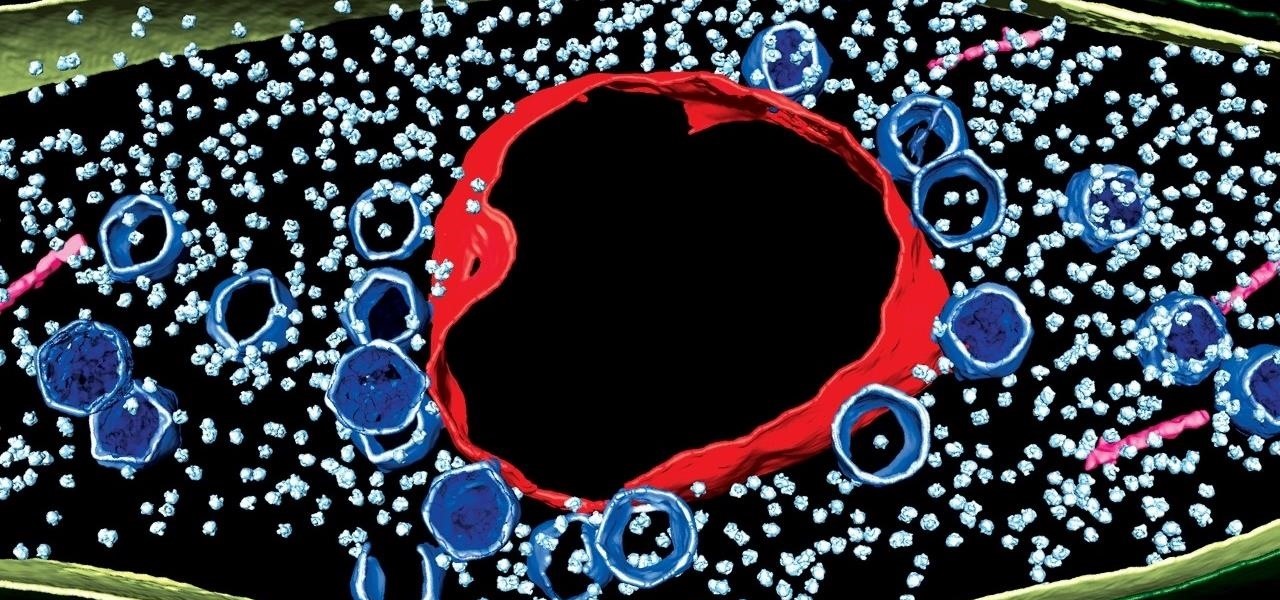
News: Viral Infections Blur the Line Between Bacteria & Complex Life Like Plants & Animals
Using extreme time-lapse microscopy, scientists watched a virus take over a bacteria to create a cell that looked and functioned more like a plant or animal cell. True story.

News: Radical Theory Linking Alzheimer's to Infections Could Revolutionize Treatment
There are all kinds of theories—many supported by science—about what causes Alzheimer's disease. Tangles of protein called ß-amyloid (pronounced beta amyloid) plaques are prominently on the list of possible causes or, at least, contributors. An emerging theory of the disease suggests that those plaques aren't the problem, but are actually our brains' defenders. They show up to help fight an infection, and decades later, they become the problem.
News: Why You Should Care About the Nevada Woman Killed by the Totally Resistant Nightmare Superbug
Humanity is standing on an infection precipice. As antibacterial resistant grows, we're running out of options, and a recent scary case of total antibiotic resistance is a frighting view of our potential future. In the end, it was septic shock that took the life of a 70-year old woman with an incurable infection. One of few such cases in the US, her death could nonetheless be the shape of things to come.

News: How Your Diet & Gut Bacteria Work Together to Reduce Risk of Colon Cancer
We all know you are what you eat—or so the expression goes—but it's good to remember that what you are (at least intestinally) is mainly bacteria. A new study has shown that what you eat, and how your gut microbiome reacts to that food, might be a key player in your risk of developing a certain type of colon cancer—and changing your diet can help decrease your risk.
News: We've Found the Back Door HIV Uses to Hide in the Brain—& It Could Help Us Take the Virus Down
Over 1.2 million people in the US are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)—and one out of eight of them don't know it. Even after decades of intense research into the virus, there's still no cure for it. One of the big problems is that the virus hides out in certain cells of the body, resisting treatments that kill it.

News: More Links Between Gut Health & Autism as 'Probiotic' Transplant Trials Show Some Success
Autism affects 1 in 68 children in the US, and that means it affects at least 1 in every 68 families. More boys than girls are diagnosed as being on the autism spectrum, and it's estimated that almost 60,000 12-year-olds in the US have autism. That is a 37-fold increase from the 1 in 2,500 children diagnosed just 30 years ago.
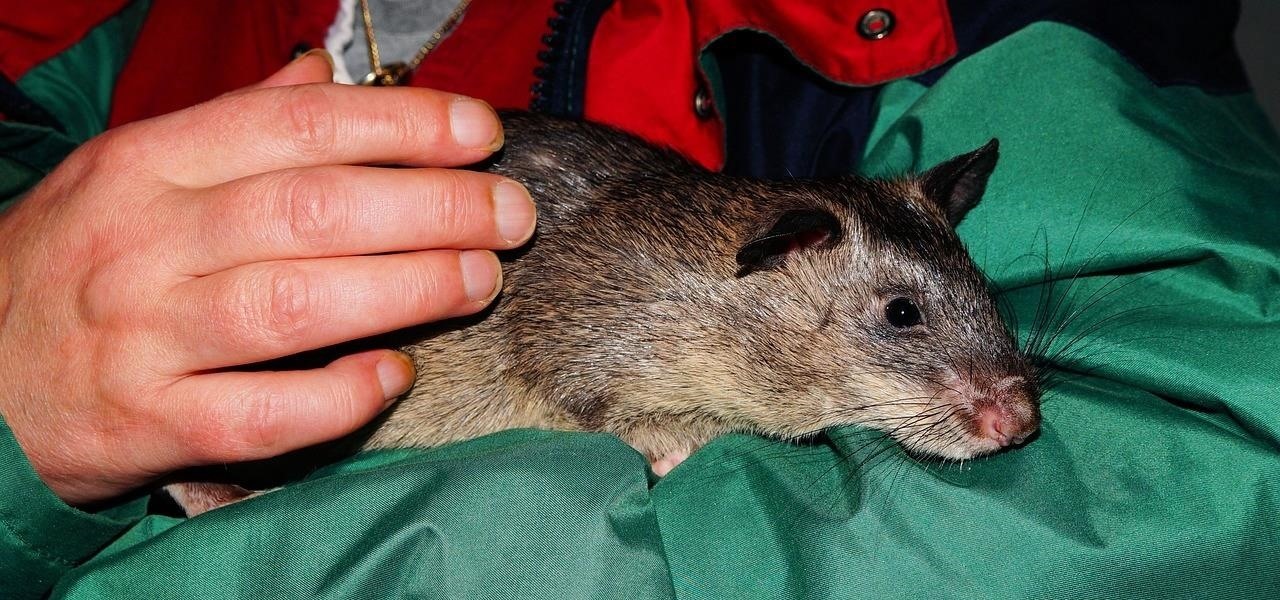

News: Rat Breeders in Illinois Are Just the Latest Victims of Unappreciated Hantaviruses That Infect Humans
A recent pathogen outbreak in Illinois is just one of many outbreaks of an underappreciated, but serious, viral infection passed from rodents to humans. These hantaviruses have been cropping up more frequently in the last decade or so, giving us more reason to clean out our dusty attics, basements, and garages.

News: Study Finds HIV Family of Viruses Far Older Than Civilization
To shine light on the future of the relationship between humans and viruses, a team of researchers from the University of Oxford looked into the dim and distant past.
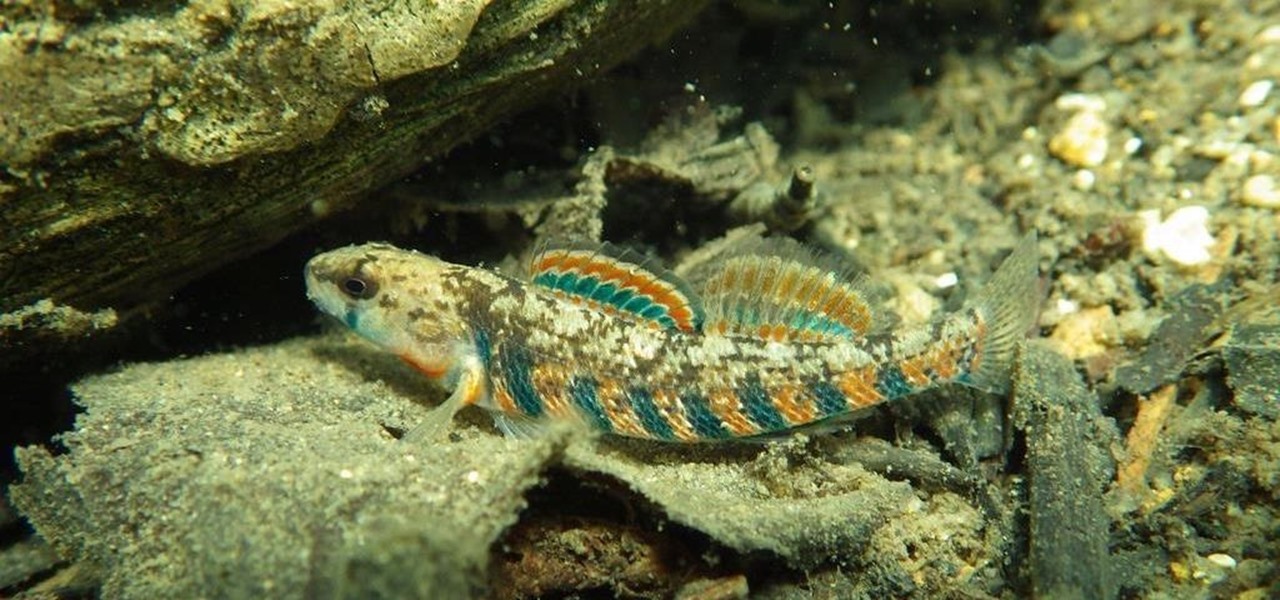

News: Sexually Confused Fish Are the Canary in the Coal Mine of Water Pollution—But Bacteria Could Come to the Rescue
Exposed to hormones, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals, the beautiful wild fish in Canada's Grand River have taken on some pretty odd characteristics—they're turning into females. A long-term study suggests using bacteria to manage polluted water could turn the tide for feminized fish.
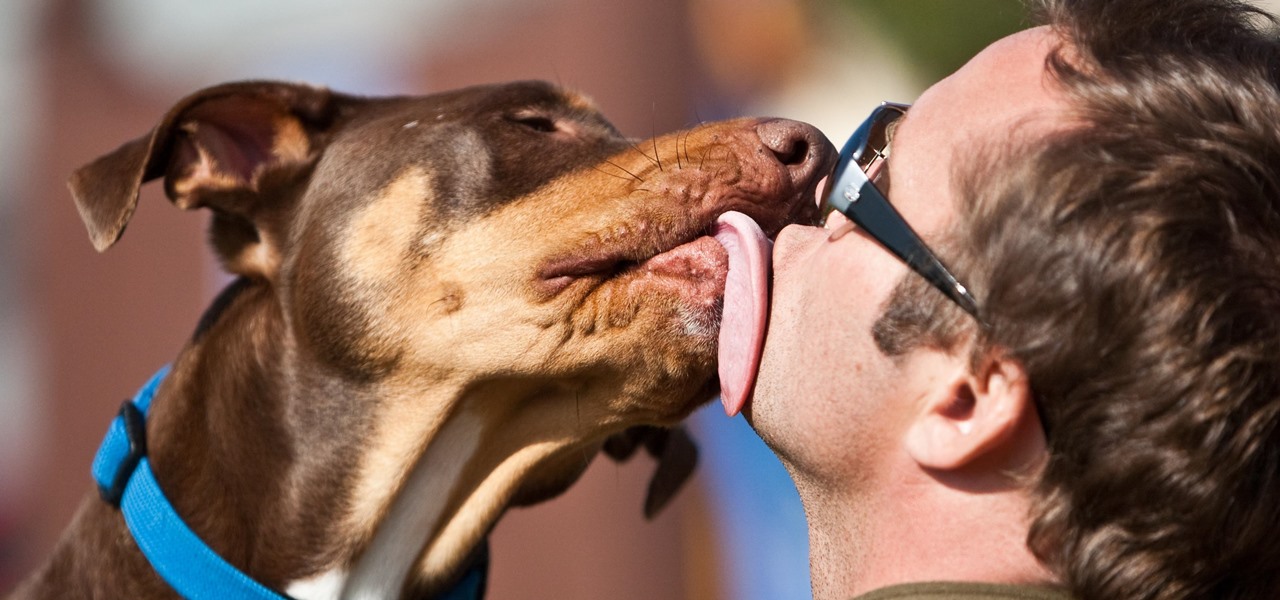

News: We Know You Want To, but You Really Shouldn't Be Kissing Your Pet on the Mouth
If you live with pets, you know where their tongue has been, yet you let them kiss and lick you all they want without even thinking twice about it. I've heard people say that a dog's mouth is very clean, and that their saliva, delivered by licking, can help heal wounds, but is that really true?

News: Cold, Dry Air Could Signal a Flu Outbreak a Week Before It Happens—Here's How to Protect Yourself
Most of us equate feeling cold with catching a virus—but we've also heard plenty of debunkers proselytizing that being cold isn't what gives you the flu.
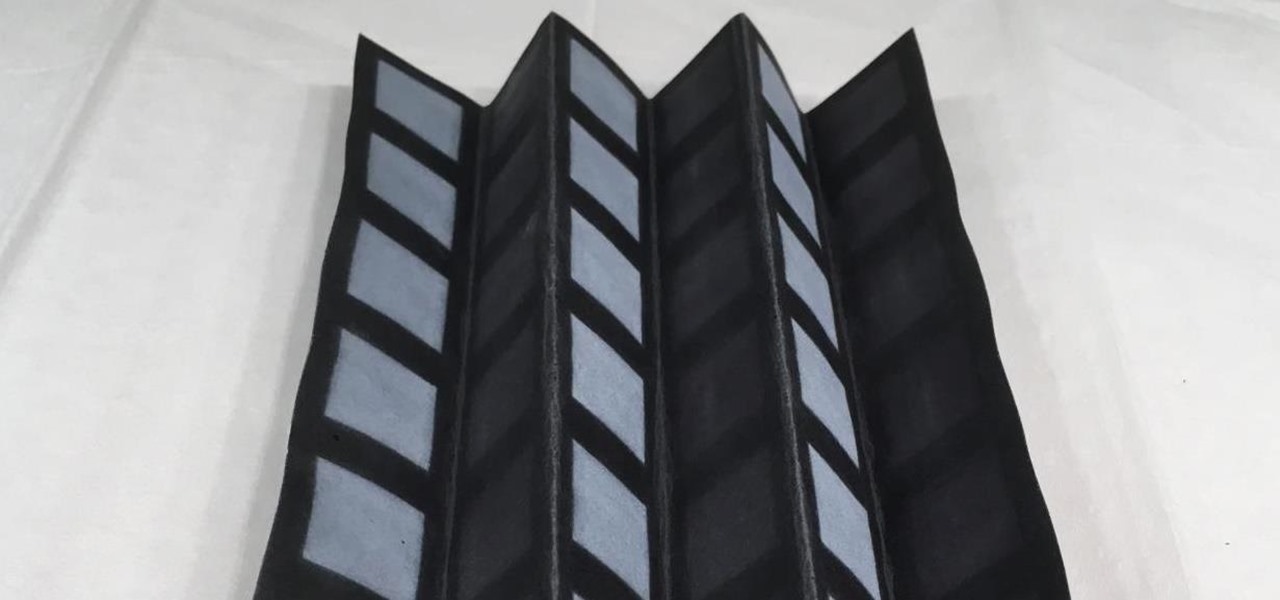

News: This Paper-Thin Foldable Battery Is Powered by Bacteria
In the perpetual search for a renewable and convenient energy source, our bacterial friends have once again stolen the limelight.

News: The Next Big Antibiotic Could Come from the Gut of an Insect
No one can dispute the evolutionary success of bugs. The oldest insect fossils were found encased in crystallized mineral silica in Scotland in 1926, and they're between 396 and 407 million years old.

News: New Coalition Investing Millions to Stop Outbreaks Like Ebola & Zika Before They Explode
Responding to the rapid emergence of dangerous pathogens around the world, a new initiative to prevent or contain pandemics was announced in Davos, Switzerland, yesterday. If you ever worried that a highly contagious pathogen could take down your community, or the country, this news is for you.
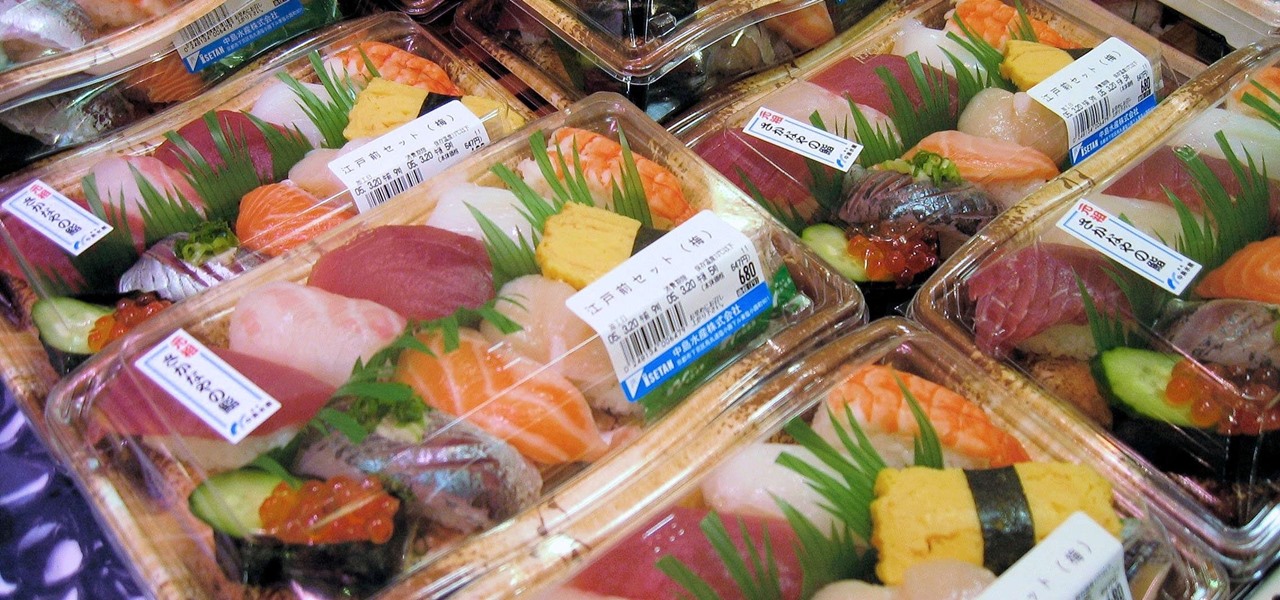

News: Thinking About Sushi Tonight? Your Raw Fish May Come with a Side of Invasive Parasite
After California college student Luis Ortiz blacked out and was taken to the hospital in 2015, doctors were startled to discover the reason his brain was swelling—a one-centimeter long, wriggling tapeworm living within a ventricle in the middle of his brain.
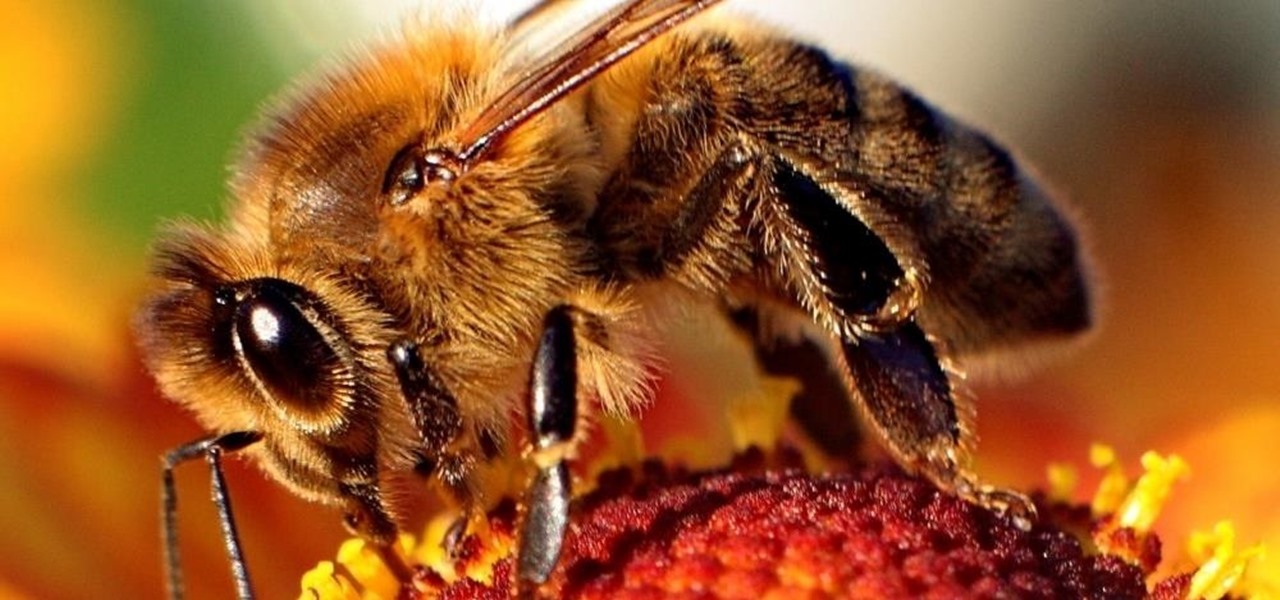

News: Say Goodbye to Almonds—Common Pesticide Additive in Orchards Linked to Honey Bee Colony Collapse
The search for the causative agent of colony collapse—the mass die off of honey bees throughout the US and Europe—has escalated with increasing confusion lately. Everything from pesticides and stress to viruses and mites have been implicated, and some researchers think that many of these environmental factors work together to take down hives.
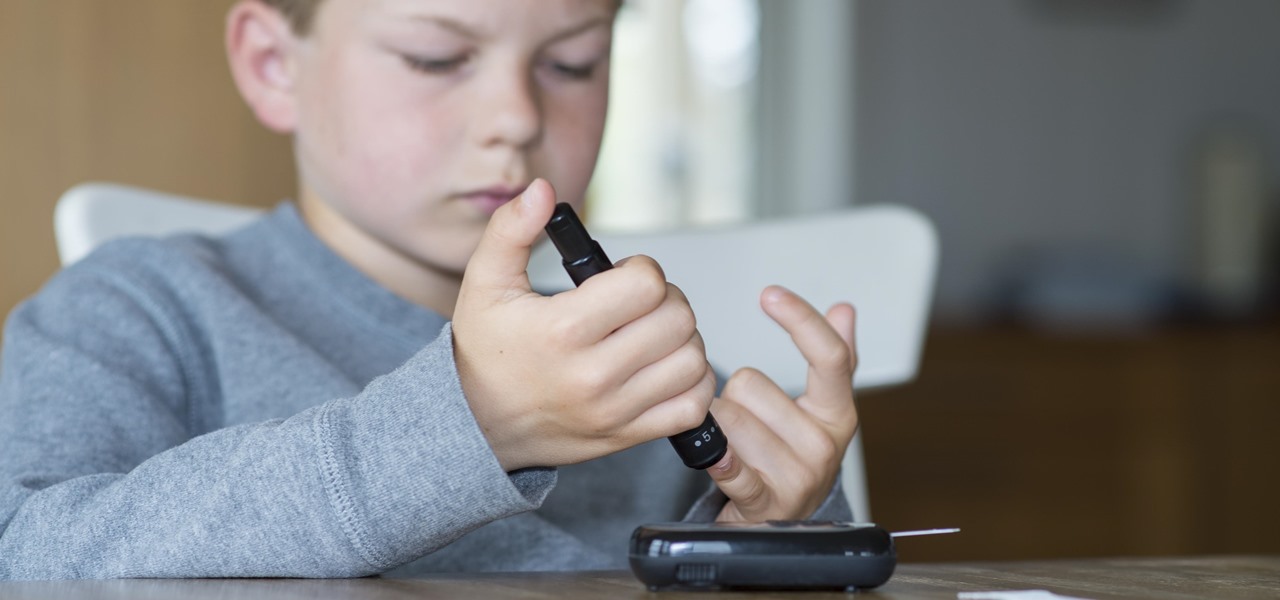

News: The Root Cause of Type 1 Diabetes Could Be a Common Childhood Viral Infection
A young child becomes very thirsty very often and seems tired all the time. A visit to the pediatrician determines she has type 1 diabetes. The onset of type 1 diabetes may seem sudden, and it can be, but the disease may actually have been triggered by common childhood viruses years earlier.

News: Hang Out with Vegans—It May Be Good for Your Bacteria, No Matter What You Eat
As researchers learn more and more about our intestinal bacteria—also called the gut microbiome—we're finding out that these microbes aren't just influencing our health and wellness, they're a useful tool for improving it, too.
News: Terrifying Superbug CRE Is Spreading Out of Hospitals
A terrifying antibiotic-resistant superbug, one thought to only infect hospital patients, has made its debut in the real world. For the first time ever, the superbug carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) infected six people who hadn't been in or around a hospital in at least a year, and researchers aren't sure how they got infected.

News: Gut May Hold Key to Infectious Brain Diseases
Specialized cells in the lining of the gut may provide a key to preventing an infectious brain disease caused by misfolded proteins.
Synthetic Biology: Student Team Gives Dangerous E. Coli a New Role as Bacteria Detective
A gold-medal winning entry into the iGEM synthetic biology competition could change the way we look at Esherichia coli, the bacteria better known as E. coli.
News: Genetically-Modified Parasites Could Save People from Malaria
You might feel the bite, you might not, but an infected mosquito has injected you with a parasite named Plasmodium falciparum, a single-cell protozoa that quickly takes up residence in your body.

News: We've Known About Zika for 70 Years — & Finally Figured Out Why It's Just Becoming a Problem
The year was 1947. Scientists had isolated a virus from a pyrexial rhesus monkey in Uganda and named it after the forest where the monkey lived — Zika.
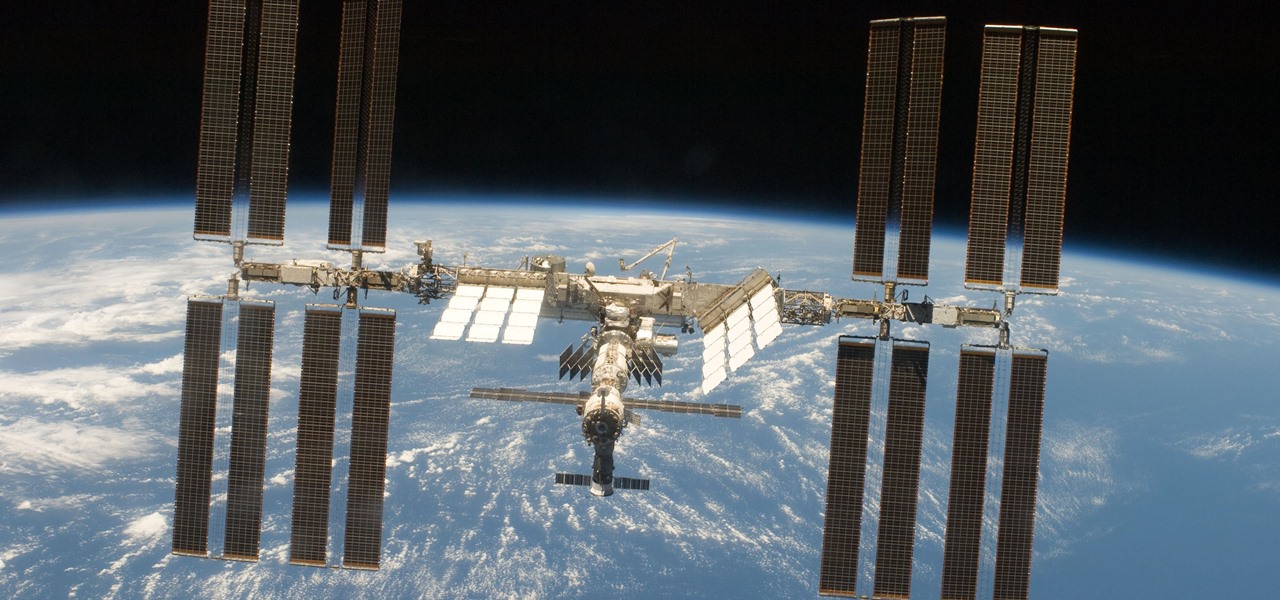

News: Microbes Behave Strangely—& Potentially Dangerously—In Space
Since the 1960s, bacteria have been hopping a ride into space on space vehicles and astronauts, and have been cultivated within experiments on space shuttles and the International Space Station (ISS). The extreme growing conditions and the low gravity environment on the Earth-orbiting vehicles offers a stable research platform for looking at bacteria in a different light.
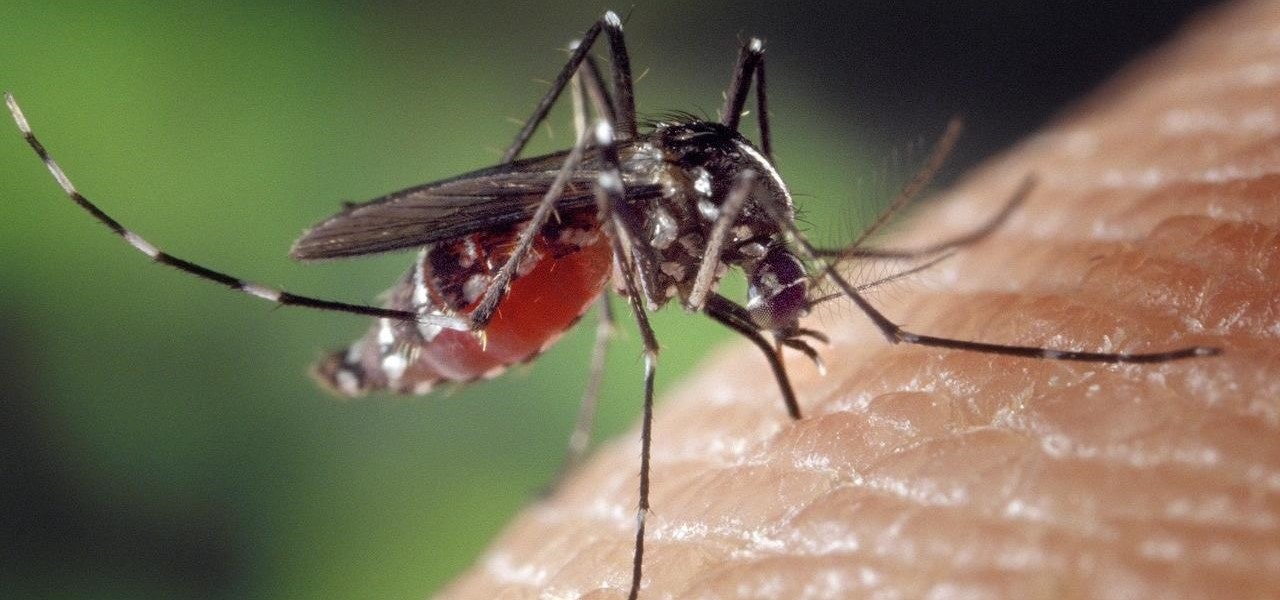
News: How El Niño—& Climate Change—Kill People with Virus Epidemics
Using mathematical modeling, researchers suggest weather and warming created the "perfect storm" that drove the Zika outbreak in 2016.
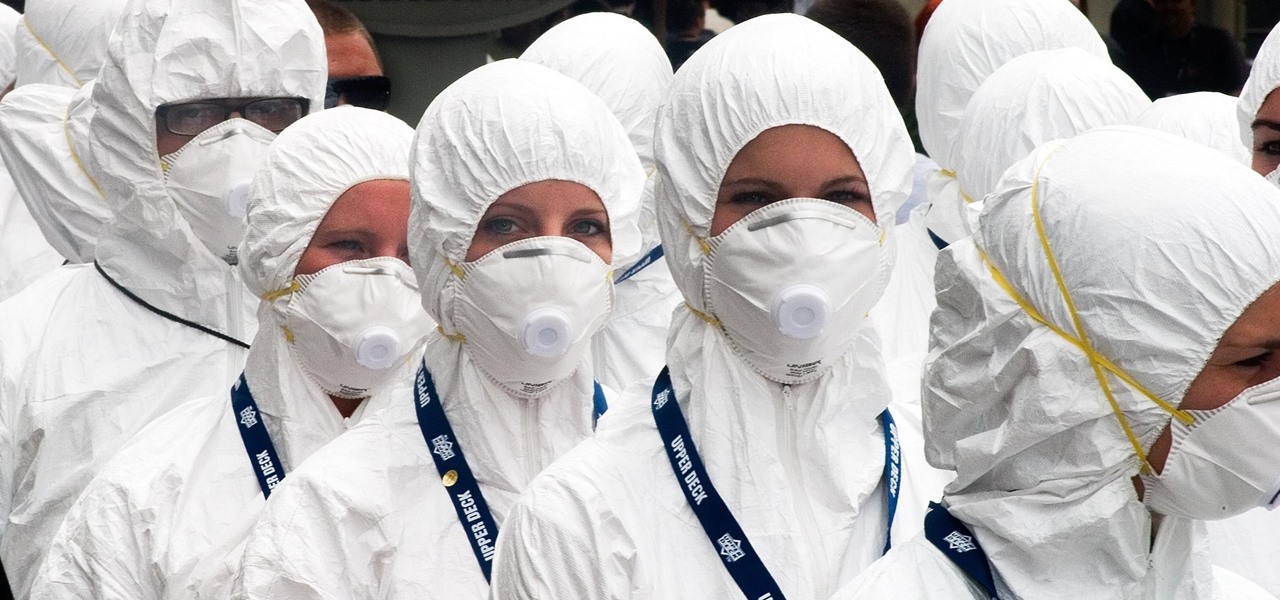

News: Do the CDC's Suggested New Quarantine Rules Give Them Too Much Power?
When Kaci Hickox, a Doctors Without Borders nurse, returned to New Jersey from working with Ebola patients in West Africa in 2014, she was surprised by her reception. Instead of a quiet return to her home in Maine after four weeks on the front line of Ebola treatment, she was quarantined by the State of New Jersey in Newark. She later filed a lawsuit in U.S. District Court for violation of her civil rights, false imprisonment, and invasion of privacy.
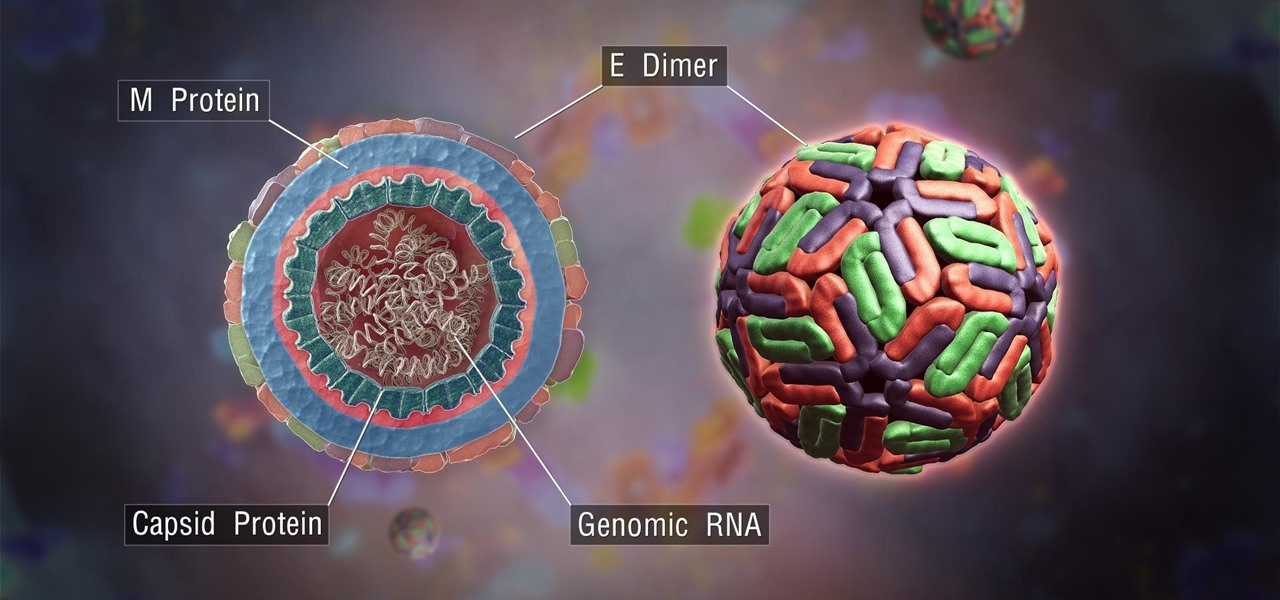
News: First Full Genome Analysis Solves the Mystery of How Zika Got So Dangerous
The mention of Zika can strike fear in the hearts of pregnant women. With infections increasing around the world, including in the US, researchers are fighting the clock to figure out how the virus can have such horrific effects in some people.
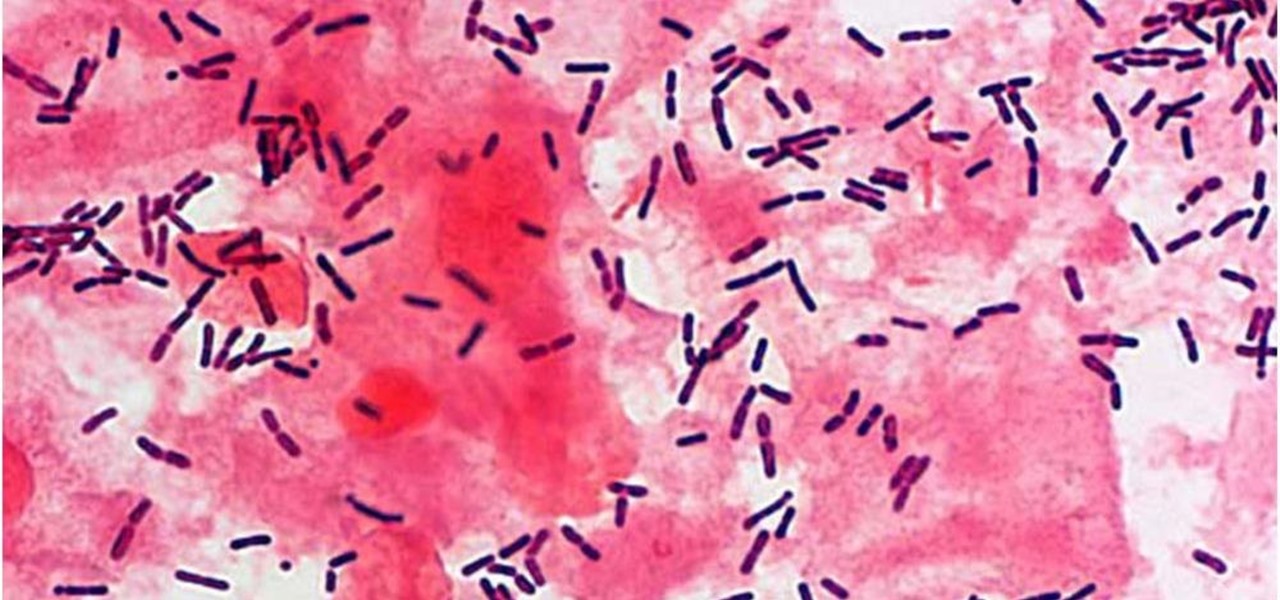
News: An Unhealthy Vaginal Microbiome Can Increase Risk of HIV Infection
The presence of certain bacteria can indicate whether the vaginal tract is healthy or not. It could also impact the likelihood of acquiring certain sexually transmitted diseases, like HIV, a new study suggests.